Running primarily enhances cardiovascular endurance and burns calories, which doesn’t significantly stress muscles enough to build them. Muscle growth typically requires resistance training or weight lifting.
Running is a popular exercise that boosts cardiovascular health and burns calories. Many people run to lose weight or improve stamina. However, those looking to build muscle might be disappointed with running alone. Muscle growth needs specific and consistent stress, usually provided by resistance training or weight lifting.
Runners may notice toned legs, but running lacks the intensity required for significant muscle hypertrophy. For balanced fitness, combining running with strength training is crucial. This approach not only builds muscle but also enhances overall health.

Credit: www.healthline.com
Introduction To Running And Muscle Building
Running is great for your heart and lungs. It helps in burning calories fast. Many believe running builds muscle. This belief is a common misconception. Running mainly works your cardio system. It does not focus on muscle growth.
Many think running can build big muscles. This is not true. Running uses aerobic energy. This energy is good for endurance. It does not help in gaining muscle size. Building muscle needs resistance training. Running does not provide this kind of training.
Building muscle is important for overall strength. It helps in daily tasks. Strong muscles support your bones. They help prevent injuries. Muscle building also boosts your metabolism. This helps in burning calories even at rest. Adding strength training to your routine is essential.
Credit: www.businessinsider.com
The Physiology Of Running
Running mainly improves the cardiovascular system. It makes your heart and lungs stronger. Your body gets better at using oxygen. This is called aerobic exercise. Running burns a lot of calories too. But it does not build big muscles. Running focuses on endurance, not muscle growth.
Muscles have different types of fibers. Slow-twitch fibers help you run for a long time. These fibers are good for endurance. They do not grow very big. Fast-twitch fibers are for quick, strong movements. These fibers get bigger with strength training. Running uses more slow-twitch fibers. This is why running does not build big muscles.
Muscle Fiber Activation
Running mainly uses slow-twitch muscle fibers. These fibers are great for endurance. They can work for a long time without getting tired. But, they do not grow much in size.
Fast-twitch fibers are different. They are used for quick, powerful movements. These fibers grow bigger and stronger. Running does not use these fibers much.
Running is an endurance activity. It trains your body to go longer and farther. This is good for heart health and stamina.
Strength activities like weightlifting build muscle size and strength. They use fast-twitch fibers. These fibers need heavy loads to grow. Running does not provide this kind of stress.
Caloric Expenditure In Running
Running uses a lot of energy. This energy comes from calories. The body burns calories to give you energy. Most of these calories come from fat and carbohydrates. Muscle fibers are not used as much. This means running does not build much muscle.
Running is great for the heart. It is also good for the lungs. But it is not the best for building muscles. Muscles need heavy weights to grow. Running does not provide this. Running uses slow-twitch muscle fibers. These fibers do not grow big. They are for endurance, not strength.
Hormonal Responses To Running
Cortisol is known as the stress hormone. Running increases cortisol levels in the body. High cortisol can lead to muscle breakdown. This makes it hard to build muscle while running. The body uses cortisol to manage stress. Running long distances can be stressful. This keeps cortisol levels high.
Growth hormone helps in muscle growth. Running does increase growth hormone. But the increase is usually small. More intense workouts boost growth hormone more. Running is often not intense enough. This limits the muscle-building effect. Short sprints can help more than long runs.
Nutrition And Recovery
Protein is key for muscle growth. Runners often focus on carbs. They need energy for long runs. Protein helps muscles repair and grow. After running, muscles need extra protein. It supports recovery and strength. Eating enough protein is crucial. Without it, muscles can’t rebuild effectively. A balanced diet is essential. Include lean meats, eggs, and beans. Dairy products like milk and cheese are good too. Protein shakes can also help. They are quick and easy. Remember to eat protein after workouts. This boosts muscle repair.
Rest is vital for muscle growth. Running causes muscle damage. Rest allows muscles to heal. Without rest, muscles stay damaged. This prevents growth. Sleep is also important. During sleep, muscles repair. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep. Rest days are as important as training days. Avoid overtraining. It leads to injuries. Recovery includes stretching. It helps muscles stay flexible. Foam rolling can reduce soreness. Listen to your body. Give it time to recover. Proper rest leads to stronger muscles.
Effective Muscle Building Strategies
Strength training is key for building muscle. It helps muscles grow stronger and larger. Running mostly works your legs, especially the calves and thighs. But it doesn’t build muscle like lifting weights does. Strength training involves lifting weights or using resistance bands. Your muscles get bigger with each session. It also includes bodyweight exercises like push-ups and pull-ups. These exercises target different muscle groups and improve overall strength.
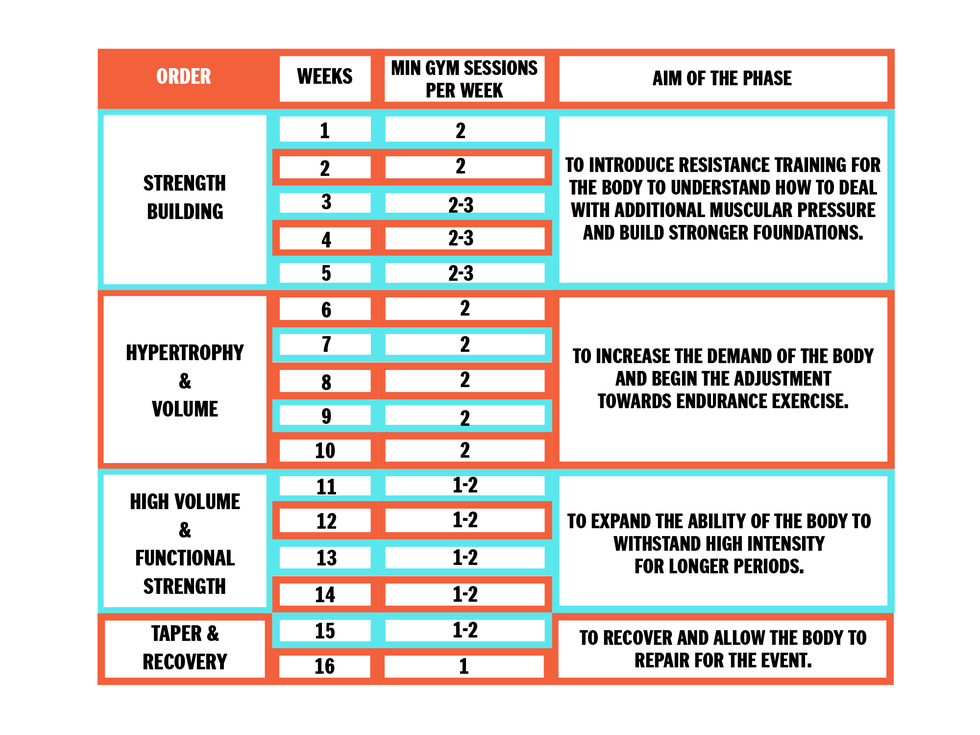
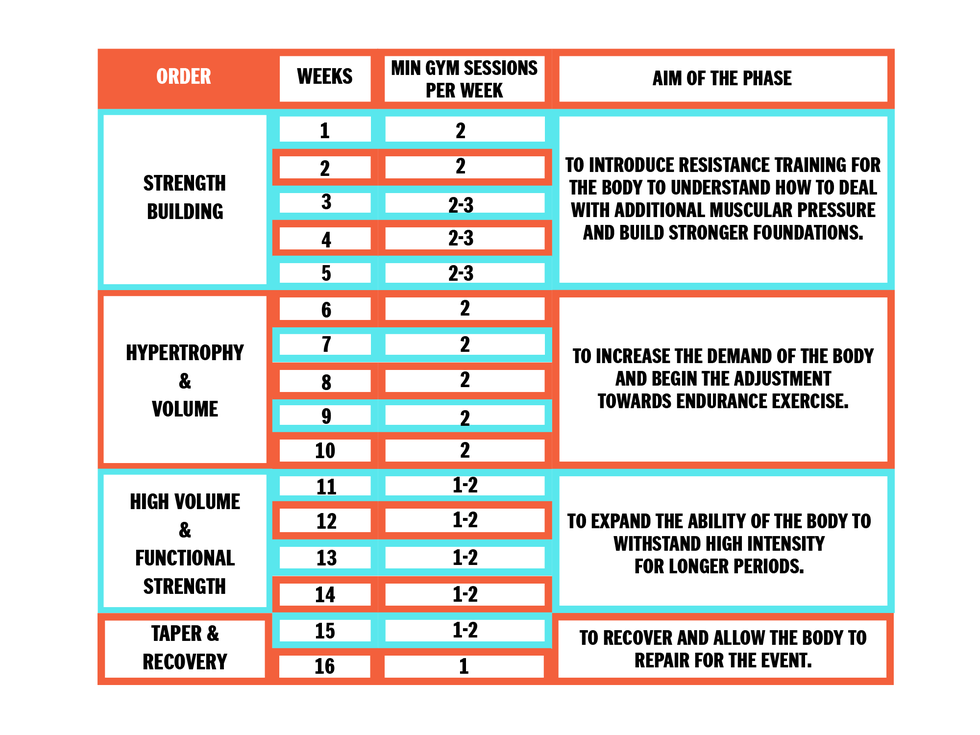
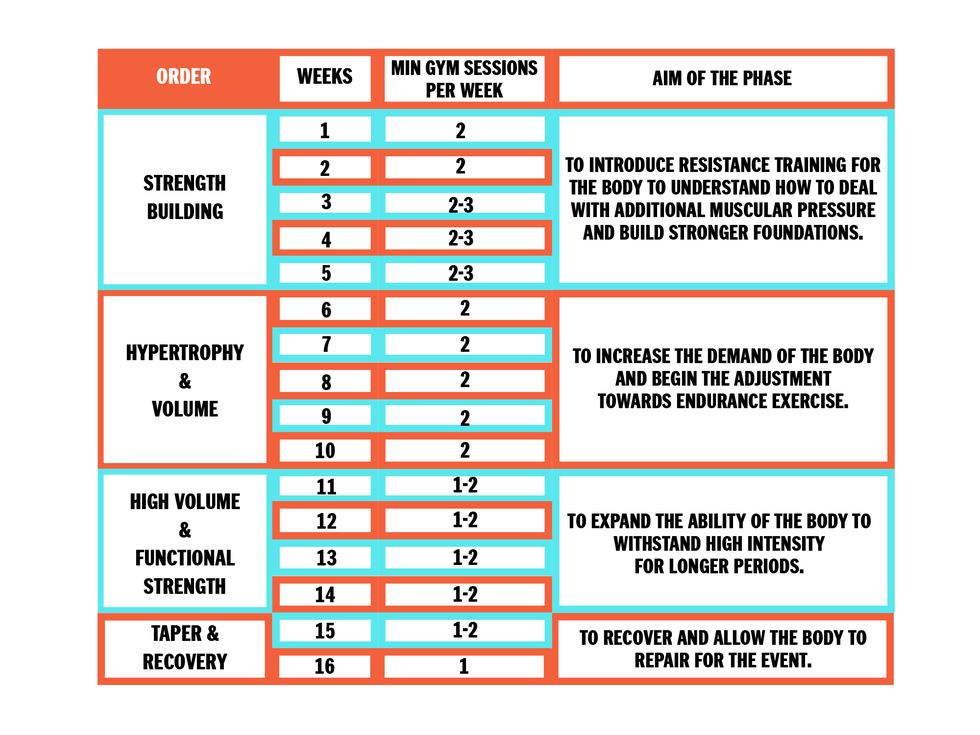
Combined workouts mix running with strength training. This approach balances muscle growth and cardiovascular health. Running helps with stamina and endurance. Strength training builds muscle and improves strength. Combining both gives the best of both worlds. Workouts could include running for 20 minutes followed by weight lifting. This keeps the body strong and fit. It also helps avoid muscle loss and improves overall fitness.
Credit: www.quora.com
Balancing Running And Muscle Building
Running is great for your heart and lungs. It helps you burn calories too. But it doesn’t build big muscles. To build muscle, you need to lift weights. You should also eat enough protein. Mixing running and weightlifting can be tricky. You need to find the right balance. Make sure you rest enough. Your muscles grow when you rest. Not during the workout. Keep track of your progress. Adjust your routine if needed.
Doing too much can harm your body. Overtraining can make you tired and weak. It can also cause injuries. Listen to your body. Stop if you feel pain. Rest days are important. They help your muscles recover. Stretching can help too. It keeps your muscles flexible. Drink plenty of water. Stay hydrated to perform well. Always warm up before running. It prepares your muscles for the workout. Cooling down is also important. It helps your muscles relax after exercise.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does Running Help Build Muscle?
Running primarily improves cardiovascular health and endurance. It doesn’t significantly build muscle mass like strength training.
Can Running Alone Build Strong Muscles?
Running alone isn’t enough for significant muscle growth. Strength training exercises are essential for building strong muscles.
Why Don’t Runners Have Big Muscles?
Runners focus on endurance, not muscle hypertrophy. Their training doesn’t promote significant muscle growth like bodybuilding.
What Type Of Exercise Builds Muscle?
Strength training, like weightlifting and resistance exercises, is effective for building muscle mass and strength.
Conclusion
Running is great for cardiovascular health but doesn’t significantly build muscle. It primarily burns calories and improves endurance. To gain muscle, incorporate strength training into your routine. Balance your workouts for the best results. Remember, consistency is key to achieving your fitness goals.
Keep pushing forward and stay dedicated.