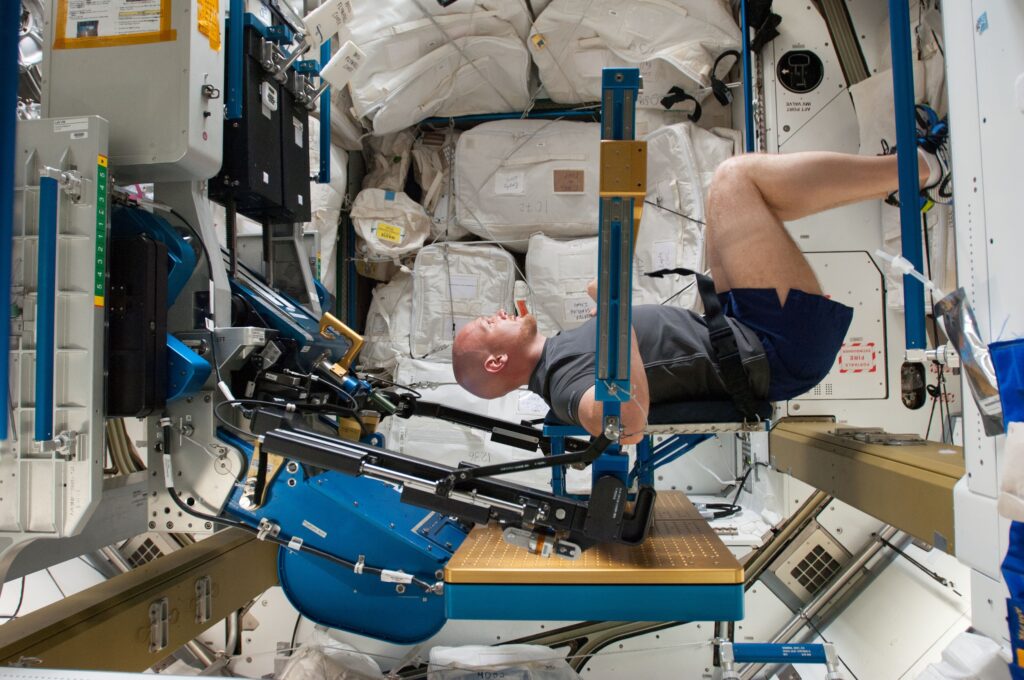
People lose muscle mass in space due to lack of gravity, which reduces muscle use and leads to atrophy. Limited physical activity further exacerbates this issue.
Muscle atrophy in space is a significant concern for astronauts. In the microgravity environment of space, muscles don’t have to work as hard to support the body, leading to muscle weakening over time. Exercise routines in space aim to counteract this effect, but they can’t fully replicate the resistance provided by Earth’s gravity.
Loss of muscle mass can impact astronauts’ overall health and their ability to perform tasks during missions. Understanding and mitigating muscle atrophy in space is crucial for long-duration space travel, ensuring astronauts remain healthy and capable throughout their missions.
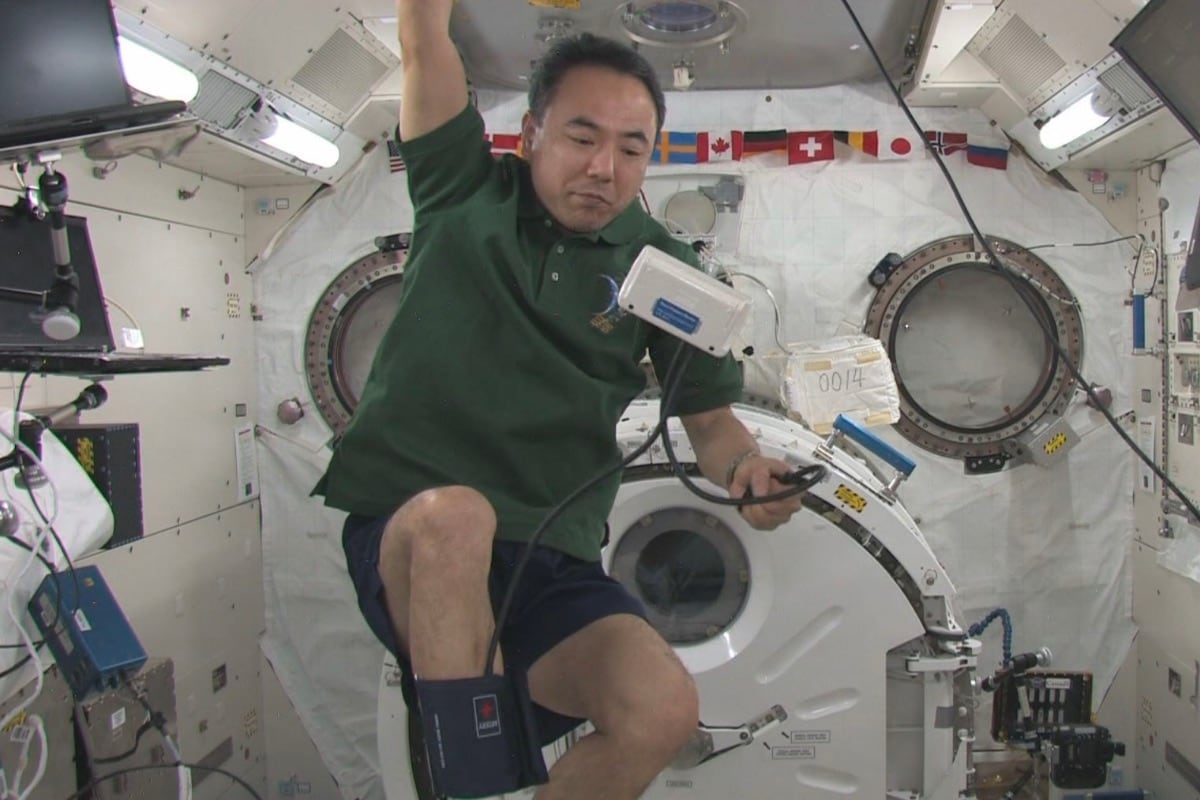

Credit: humans-in-space.jaxa.jp
Introduction To Muscle Loss In Space
Microgravity affects the body, leading to significant muscle mass loss in space. Astronauts experience reduced physical activity, causing muscle atrophy. Maintaining muscle strength becomes challenging in a weightless environment.
The Phenomenon
In space, astronauts experience microgravity. This means there is less gravity than on Earth. Muscles do not work as hard in microgravity. Muscle mass starts to decrease. This process is called muscle atrophy. Astronauts need strong muscles to stay healthy. Losing muscle can cause health problems.
Importance Of Research
Understanding muscle loss is very important. It helps scientists make better exercise programs for astronauts. These programs keep muscles strong in space. Scientists also learn how to protect muscles on Earth. This can help people who are sick or elderly.
Microgravity’s Impact
Microgravity in space leads to muscle mass loss due to reduced physical activity and lack of gravitational resistance. Astronauts experience muscle atrophy as their muscles no longer need to support their body weight. Continuous exercise and resistance training are essential to counteract these effects in space.
Reduced Physical Stress
Microgravity means there’s less pull from Earth. Muscles don’t have to work hard. Daily activities become easier in space. This leads to less physical stress on the muscles. Over time, muscles start to weaken. This is because they are not used often.
Changes In Muscle Use
In space, muscles don’t work the same way. Walking and lifting are different. Muscles that are used a lot on Earth are not needed in space. This causes those muscles to shrink. Astronauts need to exercise to keep their muscles strong. Special machines help them do this.
Physiological Changes
Muscle atrophy means muscles get smaller and weaker. In space, there is no gravity. This makes it hard to use muscles. Less use makes muscles shrink. Exercise helps, but not enough. Astronauts face this problem a lot. Strong muscles on Earth become weak in space. Keeping strength is very hard.
Bone density goes down in space. Bones need gravity to stay strong. Without it, bones lose calcium. This makes them weak and fragile. Astronauts can break bones easier. Special diets and exercises help some. But bones still get weaker. This is a big problem for long space trips.

Credit: www.facebook.com
Cellular And Molecular Effects
Muscle cells in space make fewer proteins. This affects muscle growth and repair. The body needs these proteins to stay strong. Without them, muscles become weak. A lack of exercise in space also makes this worse. Muscles need regular use to stay healthy. Astronauts try to exercise, but it’s not always enough. Reduced protein synthesis is a major factor in muscle loss.
Hormones like testosterone and growth hormone help build muscle. In space, levels of these hormones drop. Lower hormone levels mean muscles don’t grow as well. Stress hormones like cortisol can also increase. High cortisol levels break down muscle tissue. This hormonal shift makes it hard to keep muscles strong. These changes are another reason muscles shrink in space.
Countermeasures In Space
Astronauts use special exercise machines in space. These machines mimic Earth-like gravity. Daily exercise is crucial to prevent muscle loss. They perform resistance training and cardio workouts. Resistance training involves lifting weights. Cardio workouts include running on treadmills. Both types of exercise help maintain muscle strength. Exercise routines are designed by experts on Earth.
Balanced diets are essential for astronauts. They need more protein than on Earth. Protein helps build and repair muscles. Special space food contains necessary nutrients. Vitamins and minerals are also crucial. Hydration is important to maintain muscle health. Supplements may be used to meet dietary needs. Nutritionists plan meals for space missions. Proper diet supports overall health in space.

Credit: indianexpress.com
Current Research And Findings
NASA studies show that astronauts lose muscle mass in space. This happens because of the microgravity environment. Muscles do not work as hard without gravity. Exercise routines are used to help prevent muscle loss. These routines include resistance training and cardiovascular exercises.
Many space agencies work together to study muscle loss. ESA, JAXA, and Roscosmos all contribute to this research. They share data and develop new technologies. These collaborations help improve astronaut health. Scientists also study how different nationalities respond to space conditions.
Technological Innovations
Resistance exercise devices help astronauts stay strong. These devices mimic weightlifting. They use elastic bands and vacuum cylinders. Astronauts use them daily. This helps reduce muscle loss. The devices are portable. They are easy to use in space. They are crucial for muscle health.
Scientists develop drugs to fight muscle loss. These drugs help maintain muscle mass. Some hormones and supplements are tested. They may help astronauts. Research is ongoing. Safe and effective drugs are needed. This could be a game changer. Keeping muscles strong is vital in space.
Future Directions
Long missions in space lead to muscle loss. Astronauts spend months without gravity. Muscles don’t work as hard as on Earth. Exercise can help but is not enough. More research is needed. New technologies can help protect muscles. Special suits or resistance devices might work.
Combining different fields of study is key. Biologists study muscle cells. Engineers develop new exercise equipment. Physiologists explore body responses to space. Working together can find better solutions. This teamwork can help astronauts stay strong.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why Do Astronauts Lose Muscle In Space?
In microgravity, muscles don’t need to work as hard. This leads to muscle atrophy. Regular exercise is crucial to mitigate this effect.
How Does Microgravity Affect Muscles?
Microgravity reduces the need for muscle exertion. This causes muscles to weaken and shrink over time, leading to muscle loss.
Can Exercise Prevent Muscle Loss In Space?
Exercise can significantly reduce muscle loss. Astronauts follow strict exercise routines using specialized equipment to maintain muscle mass.
What Exercises Do Astronauts Do In Space?
Astronauts use resistance machines, treadmills, and stationary bikes. These exercises help maintain muscle strength and prevent atrophy.
Conclusion
Understanding muscle loss in space is crucial for long-duration missions. Weightlessness leads to muscle atrophy, impacting astronauts’ health. Countermeasures like exercise and nutrition are essential. As we aim for Mars and beyond, maintaining muscle mass will ensure astronauts’ well-being and mission success.
Future research will enhance these strategies, safeguarding our space explorers.