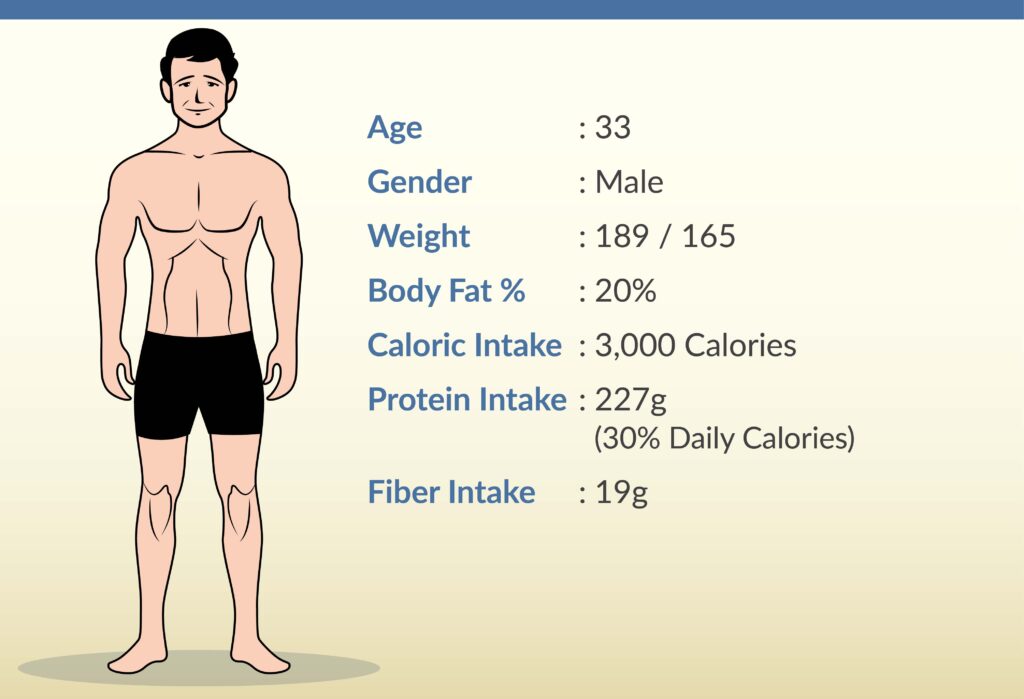
Bodybuilding food refers to nutrient-rich foods that support muscle growth, repair, and overall fitness. These foods are high in protein, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates.
Bodybuilding food plays a crucial role in muscle development. Proteins like chicken, fish, and tofu provide essential amino acids. Healthy fats from sources like avocados and nuts support hormone production. Complex carbohydrates such as brown rice and oats offer sustained energy.
Consuming these nutrient-dense foods helps in muscle recovery and growth. Proper hydration and balanced meals can optimize results. Combining these foods with a consistent workout routine enhances overall fitness. The right diet is essential for achieving bodybuilding goals and maintaining health. Effective meal planning can make a significant difference in performance and physique.

Credit: www.olympiadgenius.com
Macronutrients
Proteins help build muscles and repair tissues. They are made of amino acids. Your body needs them to grow. Good sources include chicken, fish, and beans. Eating enough protein helps you stay strong and recover quickly. Aim to eat protein at every meal. It is important for bodybuilders.
Carbohydrates provide energy for workouts. They are the body’s main fuel. Whole grains, fruits, and vegetables are great sources. Carbs help you train harder and longer. They are stored as glycogen in muscles. Eating carbs before exercise boosts performance. Choose complex carbs for lasting energy.
Fats support hormone production and brain function. They also provide energy. Healthy fats come from avocados, nuts, and olive oil. Fats help absorb vitamins. They keep you full and satisfied. Avoid trans fats and limit saturated fats. Healthy fats are essential for overall health.

Credit: www.iwm.org.uk
Micronutrients
Vitamins are vital for body building. They help in muscle repair. They also boost energy levels. Vitamin C and E are important. They protect muscles from damage. Vitamin D helps in calcium absorption. Calcium is crucial for strong bones. B vitamins help in energy production. They also reduce fatigue.
Minerals are key for muscle growth. Iron helps in oxygen transport. It is vital for muscle function. Magnesium aids in muscle relaxation. It also prevents cramps. Zinc supports protein synthesis. It is crucial for muscle recovery. Calcium strengthens bones. Strong bones support muscle training. Sodium helps maintain fluid balance. This is important during workouts.
Protein Sources
Chicken, beef, and fish are rich in protein. Eggs are a great source of protein too. Dairy products like milk, cheese, and yogurt provide protein. Animal-based proteins help build strong muscles. They are also complete proteins. This means they have all essential amino acids.
Beans and lentils are high in protein. Quinoa is a complete protein and great for vegetarians. Nuts and seeds also offer protein. Tofu and tempeh are excellent plant-based choices. Plant-based proteins are good for your heart. They are usually low in fat and cholesterol. Combining different plants can provide all essential amino acids.
Carbohydrate Choices
Simple carbs are found in sugary foods. These include candy, soda, and some fruits. They give quick energy but don’t last long. Simple carbs can cause a spike in blood sugar. They are not the best choice for long workouts. It’s best to limit simple carbs to special treats.
Complex carbs are found in foods like whole grains and vegetables. They give steady energy over time. These carbs help build muscle and fuel workouts. They also keep you full longer. Oats, brown rice, and sweet potatoes are great sources. Complex carbs are a better choice for body building.
Healthy Fats
Saturated fats are solid at room temperature. They are found in animal products and some plant oils. Meat, butter, and cheese contain saturated fats. Too much saturated fat can lead to heart disease. It is important to eat these fats in moderation. Saturated fats can be part of a balanced diet.
Unsaturated fats are liquid at room temperature. They are considered healthier than saturated fats. These fats can be found in nuts, seeds, and fish. Olive oil and avocado are good sources too. Unsaturated fats help reduce bad cholesterol levels. They support heart health and overall wellness.

Credit: issuu.com
Meal Timing
Eating a good meal before a workout is important. It provides energy and helps build muscles. A meal with carbs and proteins is best. Carbs give quick energy. Proteins help with muscle repair. Examples are chicken with rice or a banana with yogurt.
After working out, your body needs to recover. A post-workout meal helps with this. It should have proteins and carbs. Proteins repair muscles. Carbs refill energy stores. Good options are a protein shake with fruit or eggs with toast.
Supplements
Protein powders help muscles grow. They are easy to mix in shakes. Whey protein is the most common. It comes from milk. Soy protein is good for those who don’t drink milk. It comes from soybeans. Casein protein also comes from milk. It digests slowly, which helps muscles at night. Protein powders are great for a quick boost.
Vitamins and minerals are essential for the body. They keep it strong and healthy. Vitamin C helps the immune system. Vitamin D is good for bones. Iron helps carry oxygen in the blood. Calcium is also good for bones. Magnesium helps muscles work well. Eating a variety of foods gives all these nutrients.
Sample Meal Plans
Start your day with a protein-packed breakfast. Eat 3 scrambled eggs with spinach. Add a slice of whole-grain toast. For lunch, have a chicken breast salad. Include mixed greens and cherry tomatoes. Snack on a handful of almonds. Dinner should include grilled salmon and steamed broccoli. Finish with a sweet potato on the side.
For breakfast, oatmeal with berries and a scoop of protein powder. Lunch can be grilled chicken with quinoa and steamed vegetables. Snack on Greek yogurt with honey. Dinner should be lean steak with brown rice and asparagus. Before bed, have a protein shake with a banana.
Common Mistakes
Many think more food equals more muscles. This is not true. Overeating can lead to fat gain, not muscle gain. Your body needs the right amount of calories. Too many calories can slow down progress. It’s important to balance protein, carbs, and fats.
Vitamins and minerals are often overlooked. They are crucial for muscle growth. Lack of these can hinder your progress. Iron, zinc, and magnesium are very important. Always include a variety of foods in your diet. Vegetables, fruits, and nuts are excellent choices.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Bodybuilding Foods?
Bodybuilding foods are nutrient-dense items that support muscle growth and repair. They are rich in protein, healthy fats, and essential vitamins. These foods include lean meats, fish, eggs, dairy, legumes, and whole grains.
Why Is Protein Important In Bodybuilding?
Protein is vital for muscle repair and growth. It provides the amino acids needed to build muscle tissue. Consuming adequate protein helps enhance workout recovery and overall performance.
Can Vegetarians Build Muscle Effectively?
Yes, vegetarians can build muscle effectively by consuming plant-based protein sources. Foods like lentils, chickpeas, tofu, and quinoa are excellent options. Pairing these with a balanced diet ensures sufficient nutrient intake for muscle growth.
How Often Should You Eat Bodybuilding Foods?
Eating bodybuilding foods every 3-4 hours can optimize muscle growth and recovery. Frequent meals help maintain energy levels and support metabolism. This approach ensures a steady supply of nutrients for muscle repair.
Conclusion
Understanding body-building food is key to achieving your fitness goals. These nutrient-rich foods fuel muscle growth, boost recovery, and enhance performance. By choosing the right ingredients, you can optimize your diet and see remarkable improvements. Start incorporating these foods today and witness the positive changes in your body and overall health.