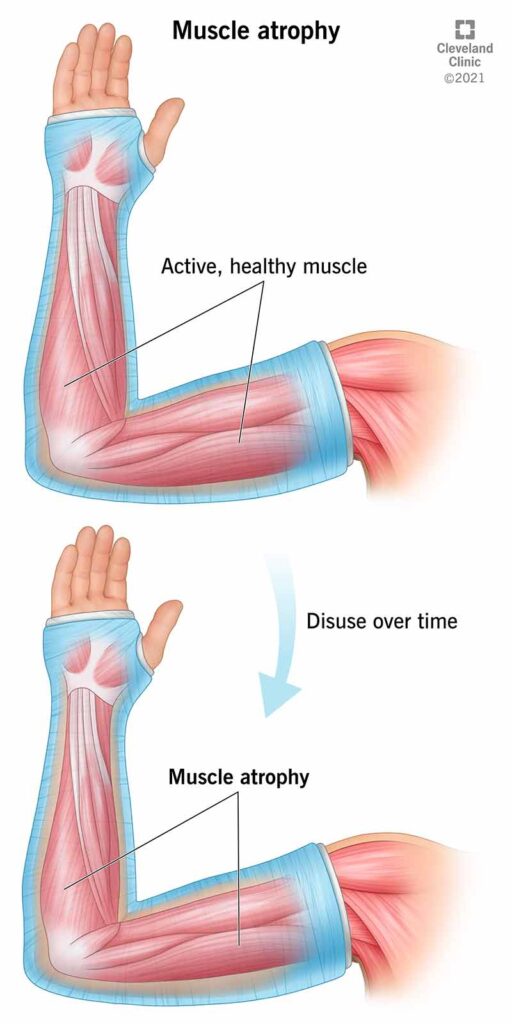
Muscle mass decreases and strength diminishes when you stop building muscle. You might experience increased body fat and reduced metabolism.
Stopping muscle-building activities impacts your body in several ways. Muscle atrophy, or the loss of muscle mass, begins quickly. This can lead to a decline in overall strength and stamina. Additionally, your metabolism may slow down, leading to potential weight gain.
Maintaining muscle mass is crucial for healthy aging, bone density, and metabolic health. Regular exercise and proper nutrition are key to sustaining muscle growth. Understanding these changes can motivate you to keep an active lifestyle. Staying consistent with your fitness routine is essential for long-term health benefits. Make muscle maintenance a priority for a healthier, more active life.
Muscle Atrophy
Muscle loss happens due to lack of exercise. A poor diet can also cause muscle loss. Aging is another reason for losing muscle. Certain illnesses can lead to muscle atrophy. Injuries and long periods of bed rest cause muscle loss too.
| Time Period | Muscle Changes |
|---|---|
| First Week | Muscles start to shrink. |
| Two Weeks | Strength decreases. |
| One Month | Noticeable muscle loss. |
| Three Months | Significant strength loss. |

Credit: www.youtube.com
Metabolic Slowdown
Muscle tissue burns more calories than fat. Stopping muscle building can slow your metabolism. A slower metabolism means you burn fewer calories. This can lead to weight gain. Your body may store more fat. Daily activities may feel harder. Energy levels can drop. Keeping your muscles strong helps maintain a healthy metabolism.
Your body burns fewer calories at rest without muscle growth. This can make it hard to maintain your weight. Even small activities burn fewer calories. Muscle loss can lead to a slower metabolism. Eating the same amount may cause weight gain. Regular exercise helps keep your metabolism active. It’s important to stay active and eat well.
Stopping muscle building increases the risk of weight gain. Your body stores more fat if you burn fewer calories. This can lead to health problems. Extra weight can strain your heart and joints. A balanced diet and regular exercise can help. Avoid unhealthy foods and stay active to maintain your weight. Keeping muscles strong is key to staying healthy.
Strength Decline
Muscles get smaller without regular exercise. This makes you feel weaker. Lifting heavy objects becomes tough. Your body loses its strong look. Bones also become less dense. This increases the risk of fractures. Keeping up with daily chores feels harder. Simple tasks like carrying groceries become a challenge.
Energy levels drop quickly. Walking up stairs feels tiring. Playing with kids becomes difficult. Even standing for long periods feels hard. Muscle loss affects your balance. You may stumble or fall more often. This can lead to injuries. Simple movements require more effort. Daily activities take longer to complete.
Mental Health Impact
Stopping muscle building can affect your mood. Physical activity helps release endorphins, which make you feel happy. Without exercise, these happy chemicals decrease. This can lead to feelings of sadness or irritability. Regular exercise also helps reduce stress. Without it, you might feel more anxious.
Muscle building often improves self-esteem. You feel proud of your progress. Stopping this can make you feel less confident. You might not like how your body looks. This can affect your self-worth. Regular exercise helps you feel strong and capable. Without it, these positive feelings might fade.
Bone Density Reduction
Muscle building helps keep bones strong. Stopping this can lead to bone density reduction. Weak bones increase the risk of osteoporosis. This condition makes bones brittle and easy to break.
Weak muscles can lead to poor balance. This raises the chance of falls and injuries. Joint pain might also increase without strong muscles. Keeping muscles active helps maintain overall health.
Cardiovascular Health
Muscles help your heart work better. Without muscle building, your heart may become weaker. A weak heart can lead to more heart health risks. You might get tired faster. Your blood pressure could go up. It’s important to keep your heart strong.
Endurance means how long you can do activities. Stopping muscle building can lower your endurance. You may find it hard to run or play sports. Your energy levels can drop. It’s easier to get out of breath. Keeping your muscles strong helps you stay active longer.
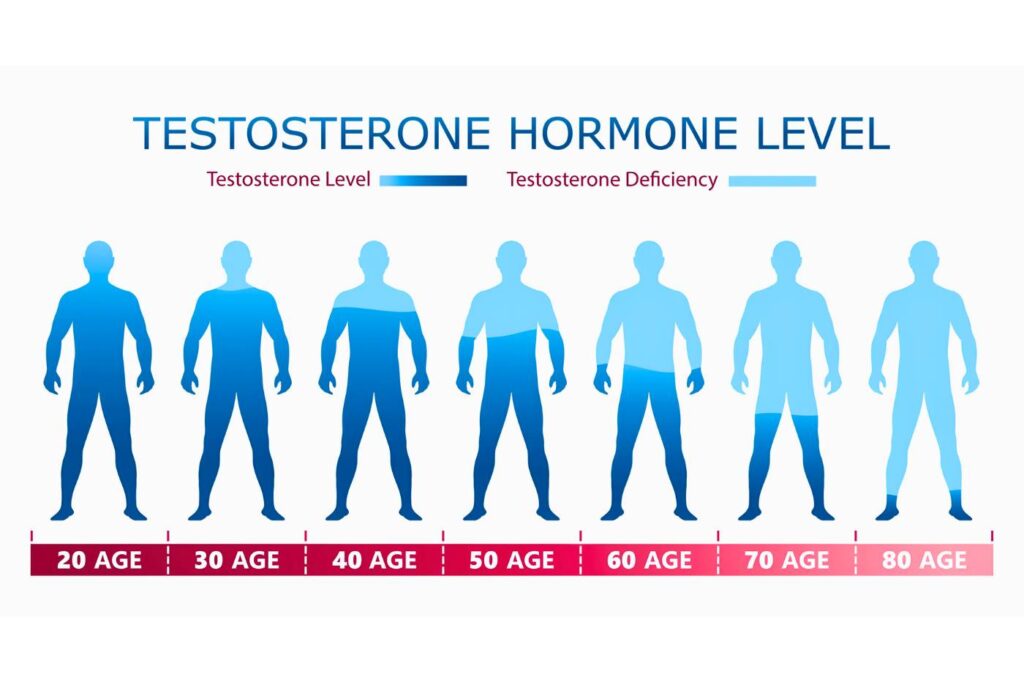
Hormonal Changes
Testosterone levels can drop when you stop building muscle. This hormone is key for muscle growth. Lower testosterone may lead to less energy. It can also affect your mood and drive. Maintaining muscle helps keep testosterone levels stable. Regular exercise boosts this hormone. Even light activity can help maintain levels.
Muscle activity improves sleep quality. Without regular exercise, sleep patterns may suffer. You might find it harder to fall asleep. Deep sleep stages might become shorter. Poor sleep affects your overall health. Good sleep helps your body recover and grow. Exercise promotes better sleep by reducing stress. Aim for at least 30 minutes of activity daily.

Credit: wichitaptgroup.com
Rebuilding Muscle
Start with light weights to avoid injuries. Focus on compound exercises like squats and deadlifts. Gradually increase the weight as you get stronger. Rest days are important for muscle recovery. Stay hydrated and eat protein-rich foods.
Consistency is key to rebuilding muscle. Regular workouts help you gain strength. Skipping workouts can slow your progress. Set a workout schedule and stick to it. Track your progress to stay motivated. Remember, patience is important.

Credit: www.facebook.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Effects Of Stopping Muscle Building?
When you stop building muscle, you may experience muscle loss and decreased strength. Additionally, your metabolism could slow down, leading to potential weight gain. Your overall physical fitness and endurance might also decline.
How Fast Do Muscles Shrink?
Muscles can start shrinking within two weeks of inactivity. The extent of muscle loss varies per individual. Regular exercise is crucial to maintain muscle mass and strength.
Can Muscle Turn Into Fat?
Muscle cannot turn into fat. They are different tissues. However, muscle loss and fat gain can occur simultaneously, leading to this misconception. Maintaining a balanced diet and regular exercise helps manage both.
Is It Hard To Regain Lost Muscle?
Regaining lost muscle is possible but may take time. Consistent resistance training and proper nutrition are key. Your body can rebuild muscle through regular exercise and adequate protein intake.
Conclusion
Stopping muscle-building efforts can lead to muscle loss and decreased strength. Regular exercise helps maintain muscle mass and overall health. Consistency is key for long-term fitness success. Keep moving and stay active to preserve your hard-earned gains. Remember, a healthy lifestyle promotes a stronger, more resilient body.