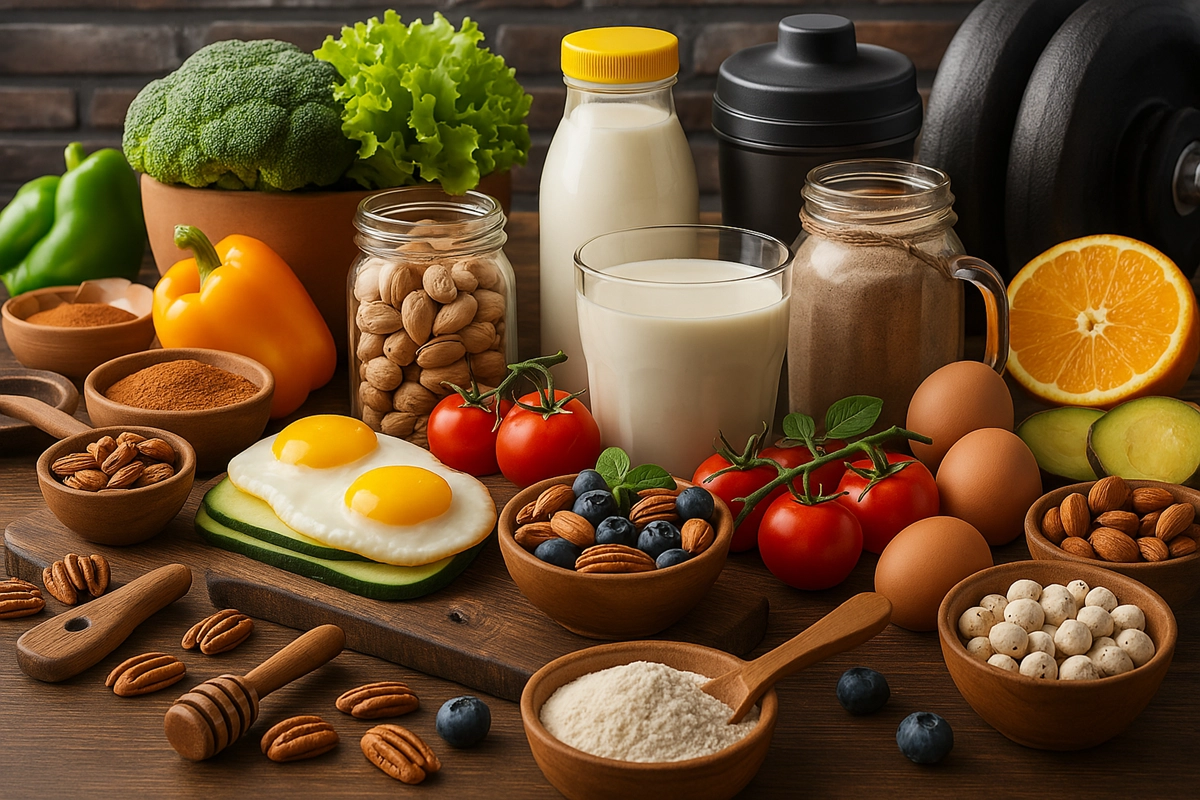
While most bodybuilders obsess over protein intake, they often overlook the vital role of saturated fats in testosterone production and muscle growth.
You’ve probably heard conflicting advice about saturated fat – some claim it’s harmful, while others suggest it’s essential for gains. The truth lies in understanding exactly how much you need and why it matters for your specific training goals.
Let’s explore the science behind saturated fat intake that even Arnold didn’t fully grasp during his prime.
What Are Saturated Fatty Acids?
Saturated fatty acids form the building blocks of many foods you’ll encounter in your bodybuilding diet. When you’re focused on optimizing protein intake and building muscle mass, understanding these fats becomes essential for your nutrition strategy.
At their core, saturated fatty acids are molecules with hydrocarbon chains that are entirely “saturated” with hydrogen atoms. Unlike unsaturated fatty acids, they don’t contain any double bonds in their structure.
Think of them as straight, rigid chains that pack together tightly, similar to how Arnold would stack his training schedule with perfect precision.
You’ll find these fats primarily in animal products, such as meat, dairy, and eggs. Their molecular structure makes them solid at room temperature, which is why butter stays firm while oils remain liquid.
Daily Saturated Fat Recommendations
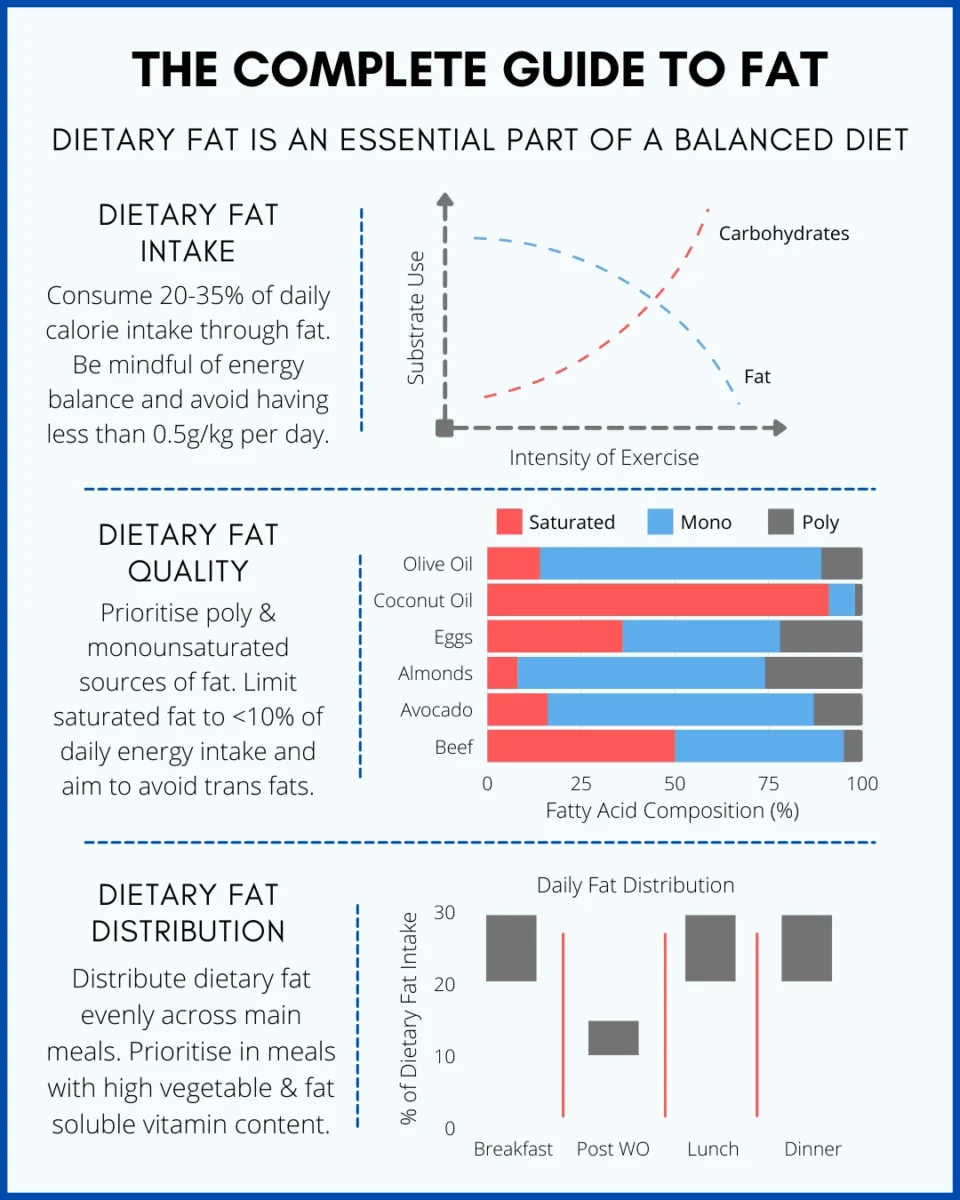
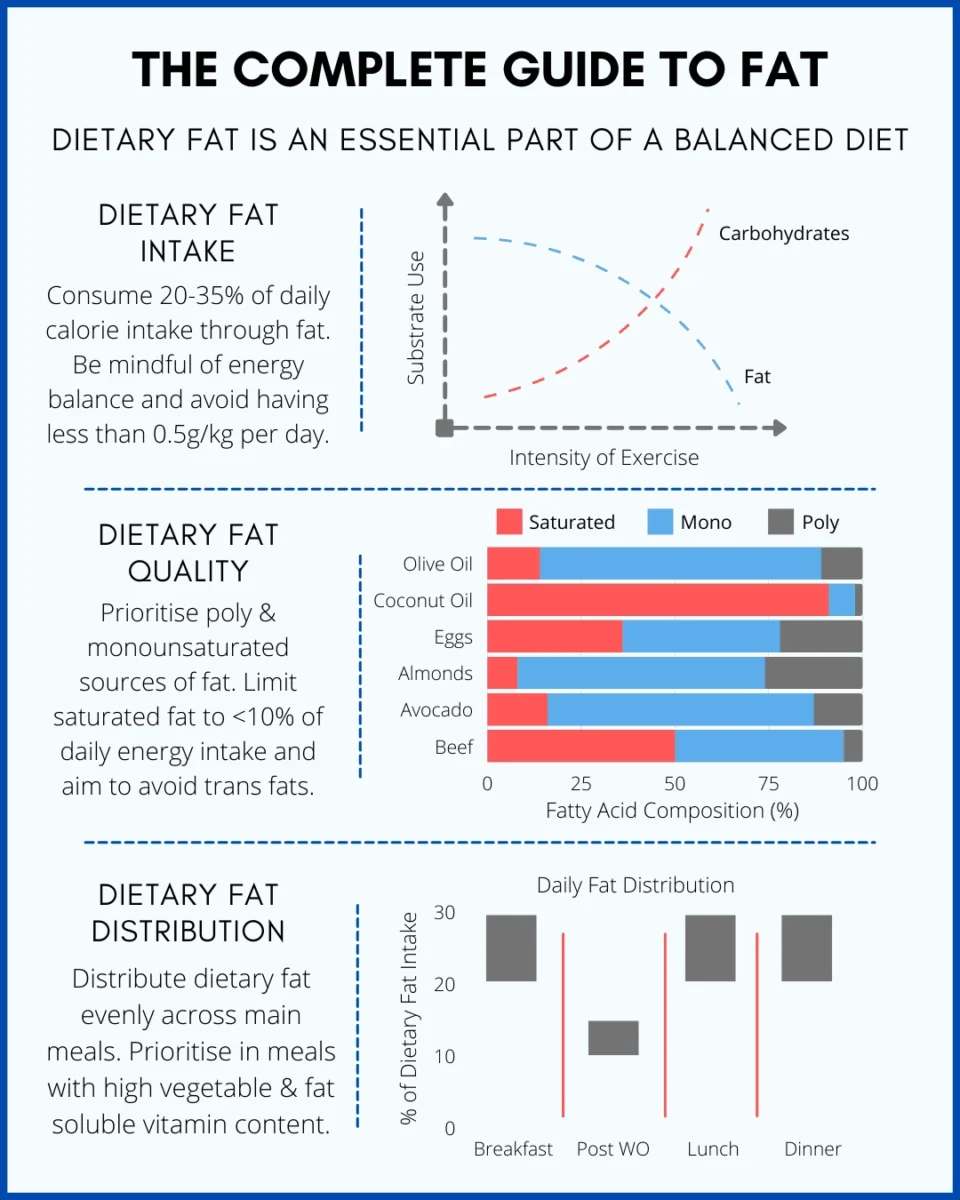
Saturated fat is essential for health. Experts suggest keeping it below 10% of daily calories. This translates to approximately 20 grams if you consume 2,000 calories per day. Overeating can be harmful to the heart. Choose healthier fats, such as olive oil and nuts.
Bodybuilders need more energy and nutrients. Saturated fat helps with hormone production. Aim for 10-15% of total calories from saturated fat. This can help build muscle and aid in faster recovery. Balance it with other healthy fats and proteins.
Why Fatty Acid Chain Length Matters
While building your perfect physique requires attention to protein and carbs, understanding the length of fatty acid chains can make or break your nutrition strategy.
When it comes to fatty acids, size matters. Short-chain and medium-chain fatty acids are quickly absorbed into your bloodstream, making them excellent energy sources for intense workouts. You’ll find these in foods like dairy and coconut oil, or you can opt for specialized MCT supplements.
Long-chain fatty acids require more complex metabolism, which isn’t always ideal for quick energy. That’s why many bodybuilders incorporate medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) into their pre-workout nutrition.
They’re easier for your body to process and can provide that immediate fuel you need to push through those extra reps, just like Arnold did during his legendary training sessions.
How Trans Fatty Acids Are Made
Now that you understand fatty acid chain lengths, let’s examine a controversial player in the nutrition game – trans fatty acids.
Trans fats occur naturally in some foods, but most of what you’ll find in processed products comes from a manufacturing process called hydrogenation. During this process, the chemical structure of fatty acids is modified, creating “trans” double bonds instead of the natural “cis” configuration.
These trans bonds force the fatty acid chain to stay straight, making it behave differently in your body. The deleterious effects of trans fats on the human body are well-documented, including lower levels of HDL (good cholesterol), elevated levels of LDL (bad cholesterol), and various cardiovascular maladies.
To protect your heart health and optimize your bodybuilding results, it’s best to minimize or eliminate trans fats from your diet.
Balancing Saturated Fat With Other Nutrients
Carbohydrates provide energy for workouts. They also aid in muscle recovery. Choose complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains and vegetables.
These carbs offer long-lasting energy. Avoid sugary snacks and drinks. They provide a quick energy spike but then lead to a crash. Whole foods are better for bodybuilding.
Proteins are crucial for muscle growth. They help repair muscle fibers after workouts. Eat lean proteins, such as chicken, fish, and eggs. Plant-based proteins, such as beans and lentils, are also beneficial. Aim for a balanced intake of proteins throughout the day. This ensures a steady supply of amino acids for muscle growth and development.
Benefits Of Saturated Fat
Saturated fat helps in muscle growth. It provides energy for intense workouts. This fat is essential for cell membranes. Strong cell membranes play a crucial role in muscle repair. Consuming the right amount boosts strength. It helps in building lean muscle mass.
Saturated fat supports hormonal balance. It aids in the production of testosterone. Higher testosterone levels enhance muscle building. This fat also helps in the creation of other hormones. Balanced hormones are vital for overall health.

Meal Planning For Bodybuilders
Breakfast includes 3 scrambled eggs and a slice of whole-grain toast. Have an apple on the side. For lunch, eat grilled chicken breast with quinoa and broccoli. Snack on a handful of almonds in the afternoon. Dinner can be salmon, brown rice, and spinach. Add a small serving of Greek yogurt for dessert.
Choose lean meats to reduce fat intake. Include healthy fats, such as avocado and nuts. Eat plenty of vegetables with each meal. Opt for whole grains instead of white bread. Stay hydrated by drinking lots of water.
Sources Of Saturated Fat
Meats like beef, pork, and lamb are rich in saturated fat. Chicken skin also contains high amounts. Dairy products such as cheese, butter, and cream are familiar sources. Eggs, especially the yolk, have some saturated fat.
Fish, such as salmon and mackerel, offer lower amounts of protein compared to red meat. Choose lean cuts to reduce intake. Always cook with healthy methods, like grilling or baking.
Coconut oil and palm oil are high in saturated fat. Cocoa butter, found in chocolate, also contains it. Some nuts, like macadamia nuts, have moderate levels. Avocados offer a mix of fats, including saturated. Use these in moderation. Balance your diet with other healthy sources of fat. Always read labels to check fat content.
How Much Saturated Fat Should We Eat?
Understanding proper saturated fat intake can significantly impact your bodybuilding progress, as these fats play a crucial role in hormone production and overall health.
For most active individuals, aim to get 25% of your total fat intake from saturated fats. If you’re consuming 80g of fat daily, that means about 20g should be saturated.
However, if you’re following a keto diet with high fat intake, you’ll need to adjust these numbers down. Conversely, those on low-fat diets should increase their saturated fat percentage to 30-40% to support hormone production.
Remember that bodybuilding diet success requires trial and error. While these guidelines provide a solid starting point, you’ll need to monitor your progress and adjust your saturated fat intake based on how your body responds.
Personalizing Saturated Fat Intake
Everyone’s body responds differently to saturated fats. Some need more, some need less. Listen to your body and adjust intake as needed. Consult a nutritionist for personalized advice. Tracking your food can help find the right balance.

Risks Of Excessive Saturated Fat
Too much saturated fat can harm your heart. It can raise harmful cholesterol levels. Bad cholesterol can clog arteries. Clogged arteries can lead to heart attacks. Your heart works harder with clogged arteries. This can cause heart disease over time.
Consuming excessive amounts of saturated fat can contribute to weight gain. Excessive weight can make it more challenging to build muscle. It can also slow down your metabolism. A slow metabolism makes it harder to lose weight. Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for achieving success in bodybuilding.
To Wrap It All Up
To achieve optimal bodybuilding results, aim for approximately 25% of your total fat intake to come from saturated fats. That means if you’re consuming 80g of total fat daily, roughly 20g should be saturated fat.
Just like Arnold Schwarzenegger maintained during his Mr. Olympia days, when he consumed approximately 4,000 calories and 100g of fat daily, proper fat ratios are essential for hormone production and muscle growth.
FAQs
What Are Saturated Fats?
Saturated fats are a type of fat with no double bonds between carbon atoms, making them solid at room temperature. They are found in animal products like meat, butter, and cheese, as well as coconut and palm oils. In moderation, they support hormone production and energy.
How Does Fat Affect Muscle Growth?
Fat affects muscle growth by supporting hormone production, especially testosterone, which promotes protein synthesis and recovery. Adequate fat intake also provides energy for training and helps absorb vitamins needed for repair. Very low fat diets can impair growth and performance.
What’s the Difference Between Saturated and Unsaturated Fat?
The main difference between saturated and unsaturated fat is their chemical structure. Saturated fats have no double bonds and are solid at room temperature, while unsaturated fats have one or more double bonds and remain liquid. Unsaturated fats are generally healthier for heart and hormone function.
Is Dietary Fat Necessary for Testosterone?
Yes, dietary fat is necessary for testosterone production. Fats, especially saturated and monounsaturated types, support hormone synthesis in the body. Very low-fat diets can lower testosterone levels, reducing strength, muscle gain, and recovery. Balanced fat intake helps maintain optimal hormone function.
Can Saturated Fat Be Part of a Healthy Diet?
Yes, saturated fat can be part of a healthy diet when consumed in moderation. It supports hormone production and provides energy. Limit intake to less than 10% of daily calories and prioritize whole food sources like eggs, dairy, and coconut oil to reduce health risks.
What Foods Are High in Saturated Fat?
Foods high in saturated fat include red meat, butter, cheese, cream, coconut oil, and palm oil. Processed foods like pastries, ice cream, and fried items also contain high levels. These should be eaten in moderation to support health while maintaining balanced fat intake.
Is Saturated Fat Good or Bad for Testosterone?
Saturated fat is good for testosterone when consumed in moderation. It supports the production of steroid hormones, including testosterone. Diets too low in saturated fat may reduce hormone levels, while excessive intake can increase cardiovascular risk. Balance is key for hormonal and heart health.
Should Bodybuilders Avoid Saturated Fat?
Bodybuilders should not avoid saturated fat entirely. Moderate intake supports testosterone, energy, and recovery. Avoiding it completely can impair hormone production. Instead, include whole food sources like eggs, red meat, and dairy while limiting processed saturated fats to protect heart health.