To train for strength, focus on low repetitions with heavy weights. Prioritize compound movements like squats, deadlifts, and bench presses.
Strength training emphasizes the ability to lift heavier weights rather than increasing muscle size. This method involves lifting weights at high intensity with fewer repetitions. Compound movements engage multiple muscle groups, promoting overall strength. By concentrating on proper form and progressively increasing weight, you can build a solid foundation of strength.
Consistency and proper recovery are crucial to prevent injuries and ensure steady progress. Incorporate rest days and balanced nutrition to support muscle repair and growth. This approach not only enhances physical power but also improves functional fitness, making everyday tasks easier.
Introduction To Strength Training
Train for strength by focusing on low reps with heavy weights. Prioritize compound movements like squats and deadlifts. Maximize gains through progressive overload and proper recovery.
Differentiating Strength And Hypertrophy
Strength training focuses on increasing power. Hypertrophy training focuses on muscle size. Strength training uses heavier weights. Hypertrophy training uses lighter weights and more reps. Strength training has longer rest periods. Hypertrophy training has shorter rest periods. Strength training improves functional fitness. Hypertrophy training improves muscle appearance.
Benefits Of Focusing On Strength
Focusing on strength increases overall power. It helps in daily tasks. Strength training improves bone health. It also enhances joint stability. Strength training boosts metabolism. It can lead to better athletic performance. It reduces the risk of injuries. Focusing on strength builds mental toughness. It provides long-term health benefits. Strength training is suitable for all ages.

Fundamentals Of Strength Training
Master the basics of strength training by focusing on heavy weights and low repetitions. Prioritize compound movements like squats and deadlifts for maximal efficiency.
Neural Adaptations Vs. Muscle Growth
Strength training focuses on neural adaptations. These are changes in how your brain and muscles talk. This makes you stronger without getting bigger. Muscle growth is also called hypertrophy. This means your muscles get bigger. Strength and size are not the same. To get stronger, use heavy weights and fewer repetitions. This will make your nerves more efficient.
Type Ii Muscle Fibers And Power
Type II muscle fibers are key for strength. These fibers are fast and strong. They help you lift heavy weights quickly. Training these fibers will improve your power. Use explosive movements to train them. Examples include sprints and jumps. Type II fibers do not grow as much in size. This helps you stay lean while getting strong.
Designing A Strength-not-size Program
Focus on compound exercises. These include squats, deadlifts, and bench presses. Such exercises work multiple muscle groups. This helps you build overall strength. Isolation exercises are less effective for strength. Use free weights like barbells and dumbbells. Machines limit your range of motion. A wide range of motion boosts strength.
Aim for low reps and high weight. Perform 3-5 sets of 3-5 reps. This method builds power. Rest for 2-5 minutes between sets. Rest helps your muscles recover. Recovery is key for lifting heavy weights.
Optimal Nutrition For Strength Athletes
Strength athletes need a balanced diet. Protein is crucial for muscle repair. Aim for 1.6-2.2 grams of protein per kg of body weight. Carbohydrates provide energy for workouts. 4-7 grams of carbs per kg is ideal. Fats support hormone production. Intake should be 0.5-1 gram per kg. Balance these ratios for optimal strength gains.
Creatine boosts short bursts of strength. Take 3-5 grams daily. Beta-Alanine enhances endurance. 2-5 grams daily can help. Whey protein aids muscle recovery. 20-30 grams post-workout is effective. BCAAs reduce muscle soreness. 5-10 grams during workouts can benefit. Choose supplements wisely for maximum strength.
Leveraging Progressive Overload
Progressive overload helps muscles grow stronger. Add small weights regularly. Lift heavier each week. Your muscles adapt to the new weight. This makes you stronger over time. Never rush the process. Slow and steady wins the race. Track your progress in a journal. Write down each weight increase. Celebrate small victories. Consistency is key for success.
Rest days are crucial for muscle growth. Muscles need time to repair. Overtraining can lead to injuries. Always get enough sleep each night. Sleep helps muscles recover faster. Hydrate well to keep muscles healthy. Eat protein-rich foods for muscle repair. Stretch before and after workouts. Stretching prevents stiffness and soreness. Listen to your body. Take breaks when needed.
Incorporating Periodization
Periodization means changing your workout plan regularly. This helps your body to grow stronger. You can change how hard you train every few weeks. For example, train hard for three weeks. Then train less hard for one week. This keeps your muscles guessing and growing. It also helps to avoid injuries.
A deload phase means a short break from hard training. During this time, you lift lighter weights. This gives your body time to recover. It helps to prevent burnout and injuries. A deload phase should last about one week. It keeps you strong and healthy for the long term.
Mind-muscle Connection In Strength Training
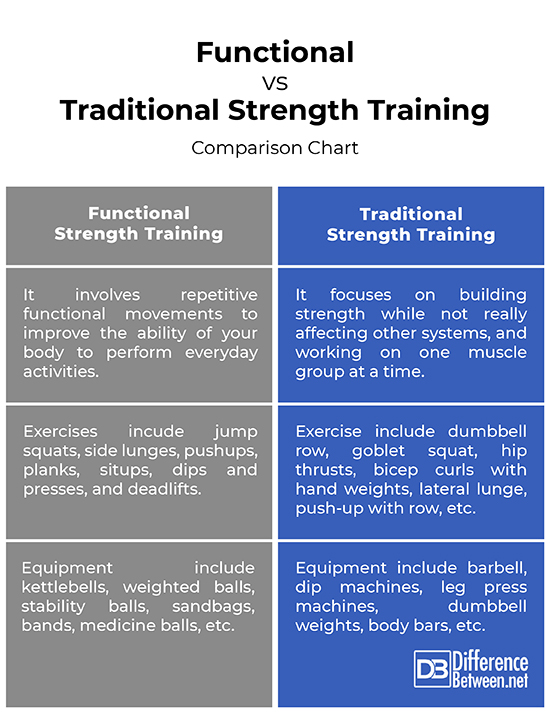
Focus on proper form instead of lifting heavier weights. Slow and controlled movements activate more muscle fibers. Use a mirror to check your posture. Ask a trainer to watch your form. Poor technique can lead to injuries. Always warm up before lifting. Use lighter weights to perfect your form. Never sacrifice technique for heavier weights. Your muscles should feel the workout.
Proper breathing helps lift more weight. Breathe in before you lift. Hold your breath while lifting. Breathe out after you complete the lift. Use the Valsalva maneuver for heavy lifts. Tighten your core while lifting. This helps stabilize your spine. Never hold your breath too long. It can cause dizziness. Practice deep breathing to improve your lifts.
Advanced Strength Training Techniques
Plyometrics help build strength and power. They include jumping and bounding exercises. These movements require speed and force. Explosive movements like sprints and box jumps are effective. They increase muscle activation and power output. These exercises also improve neuromuscular coordination. Start with low intensity and gradually increase.
Isometric exercises involve holding a position without moving. They build peak strength and muscle endurance. Examples include planks and wall sits. These exercises target specific muscles. Hold each position for 10-30 seconds. Gradually increase the duration over time. Isometrics are great for joint stability. They also improve muscle control and tendon strength.
Common Myths In Strength Training
Strength training does not always lead to muscle size. Lifting heavy weights helps build strength, not bulk. Many think more reps mean more size. High reps can increase size, but not always strength. Strength comes from neural adaptations, not muscle growth. Heavy weights and low reps build power, not muscle size.
Cardio is important for overall health. It does not hurt strength gains. Cardio helps with recovery and stamina. Short bursts of high-intensity cardio can boost strength. Balanced training includes both cardio and weights.
Measuring Progress And Success
Use a workout log to track your lifts. Record the weight lifted and the number of reps. This helps you see your improvements over time. It’s important to stay consistent with your workouts. Consistency leads to steady progress. Always warm up before lifting heavy weights. This prevents injuries and prepares your muscles.
Set small, achievable goals for each workout. Celebrate each goal you reach. This keeps you motivated and focused. Make sure your goals are specific. Instead of saying “get stronger,” aim to increase your squat by 10 pounds in a month. Adjust your goals as you progress. This helps you stay challenged and engaged.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can You Build Strength Without Size?
Yes, you can build strength without increasing size. Focus on low-rep, high-weight training and improve neuromuscular efficiency.
How Do You Train For Strength Vs Size?
To train for strength, lift heavier weights with lower reps (1-5). For size, use moderate weights with higher reps (8-12). Focus on compound movements for strength and incorporate isolation exercises for size. Rest longer for strength and shorter for hypertrophy.
How Can I Strength Train Without Getting Bulky?
Focus on using lighter weights with higher repetitions. Incorporate compound exercises to build lean muscle. Maintain a balanced diet and include cardio. Avoid excessive calorie surplus.
How Many Reps For Strength Not Size?
For strength, aim for 4-6 reps per set. Use heavier weights and focus on proper form and technique.
What Is Strength Training?
Strength training focuses on increasing muscle power and force. It emphasizes heavy weights and low repetitions.
How Often Should I Strength Train?
Train 2-3 times per week. Allow rest days in between sessions for recovery.
What Exercises Are Best For Strength?
Compound exercises like squats, deadlifts, and bench presses are essential. They engage multiple muscle groups.
Do I Need Heavy Weights For Strength?
Yes, heavy weights are crucial. Aim for 70-85% of your one-rep max to build strength.
Should I Increase Weight Or Reps?
Increase weight gradually. Focus on low repetitions, around 3-6 per set, to build strength effectively.
Is Diet Important For Strength Training?
Absolutely, a balanced diet rich in protein supports muscle repair and growth. Stay hydrated and eat nutrient-dense foods.
Conclusion
To train for strength, focus on low reps and heavy weights. Prioritize compound movements like squats and deadlifts. Maintain proper form to prevent injuries. Rest and recovery are crucial for muscle growth. Consistency and discipline will yield the best results.
Follow these tips to build lasting strength effectively.