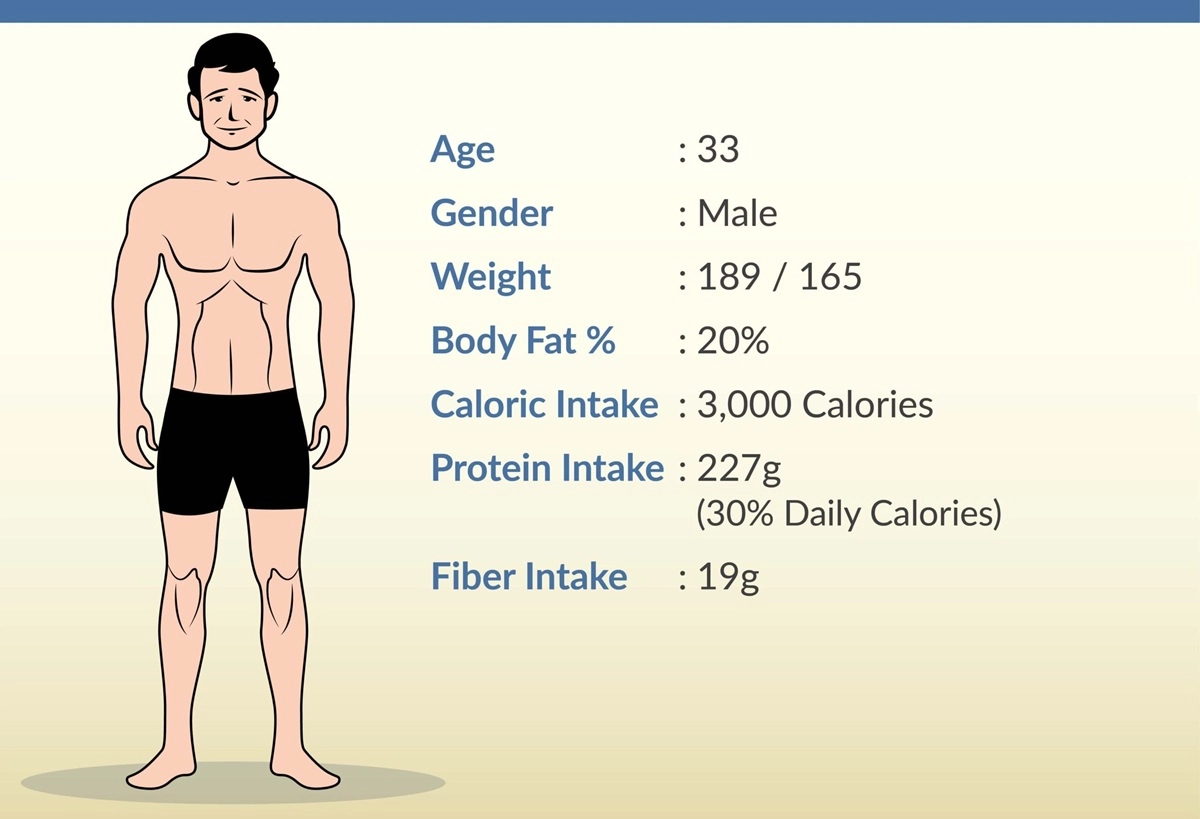
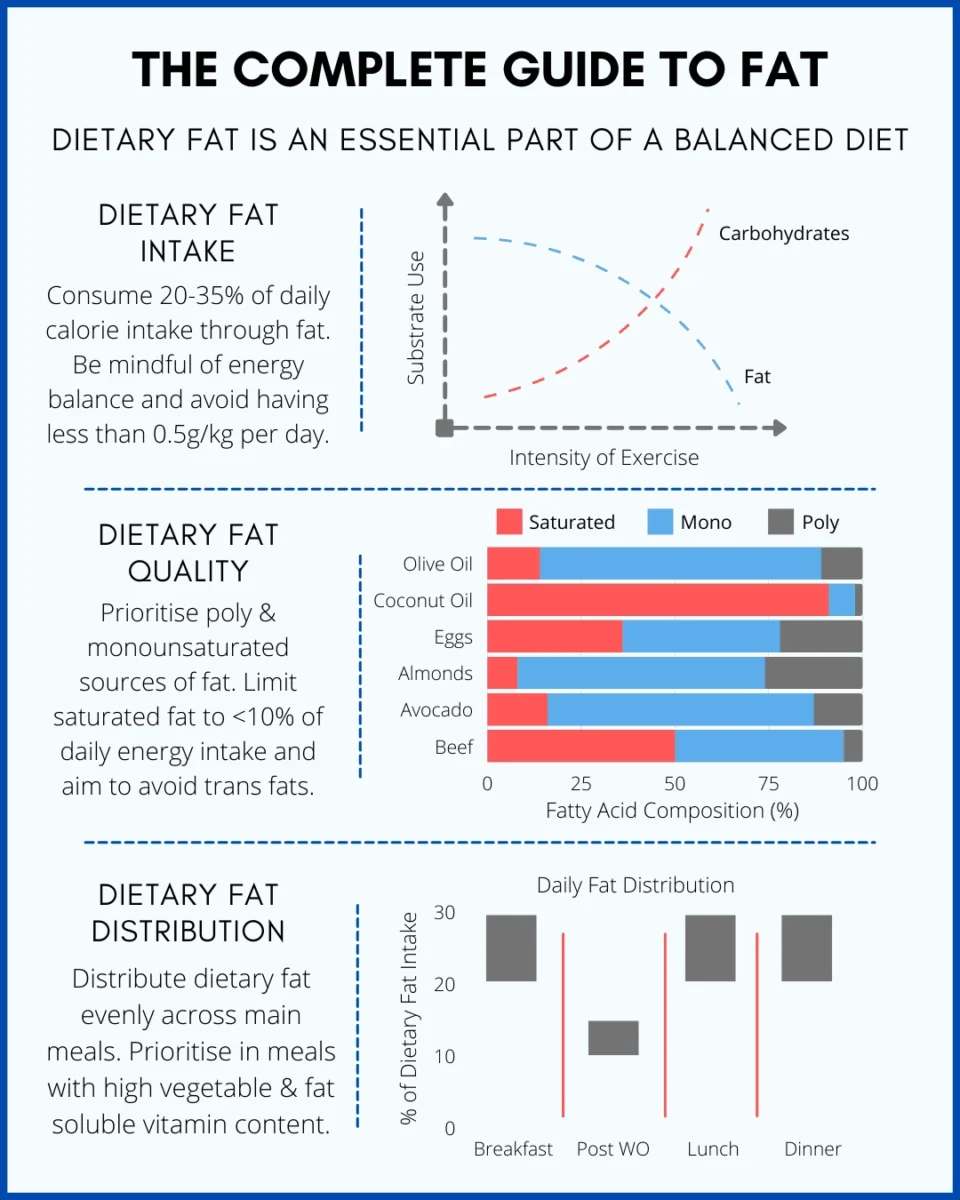
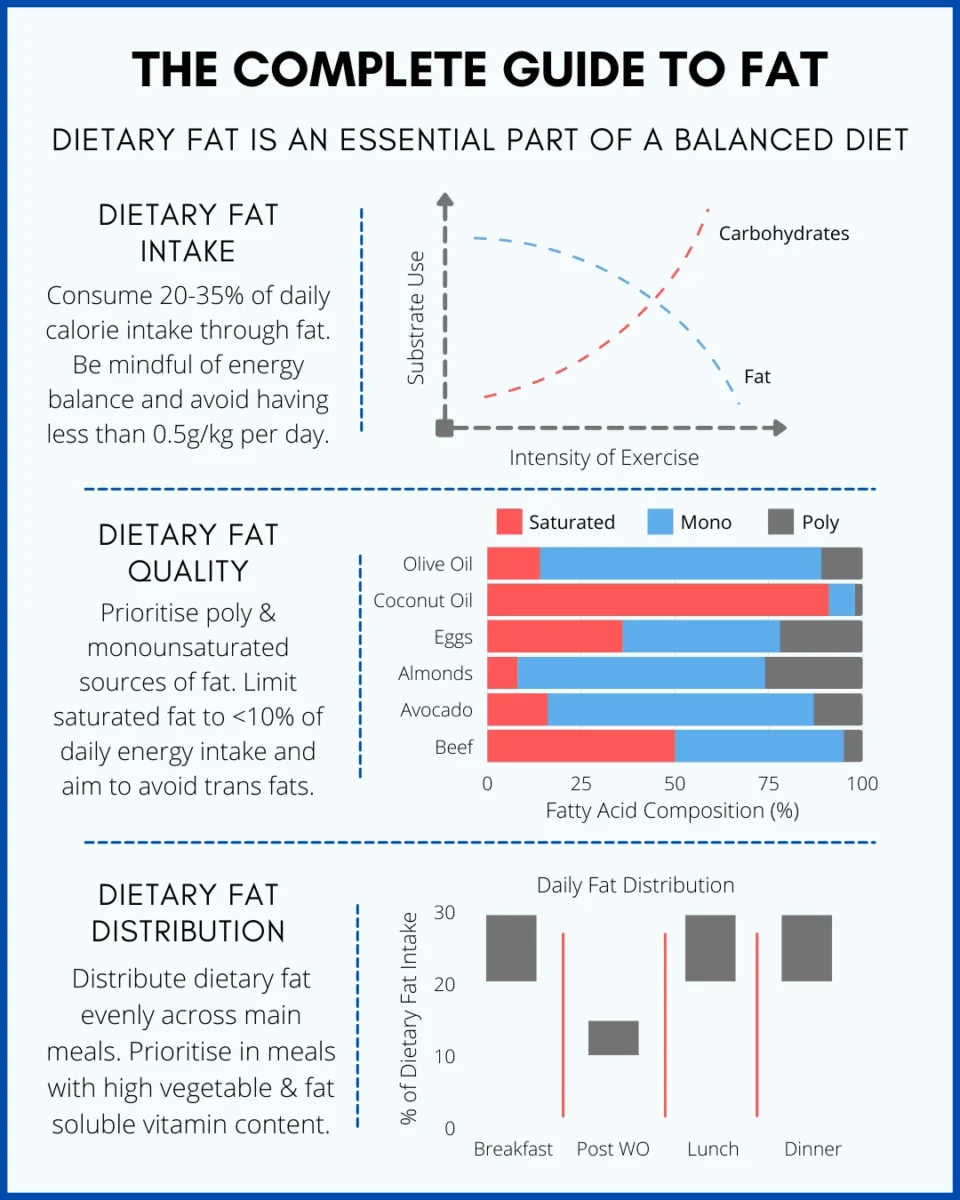
When you’re pursuing bodybuilding, determining your ideal caloric intake isn’t just about eating more – it’s about eating smart.
Your body’s energy needs depend on several key variables, from your current physique to your specific fitness goals.
Even Arnold Schwarzenegger knew that strategic nutrition was essential, famously stating that “muscles are built in the kitchen.”
Understanding how to calculate and adjust your calories will make the difference between gaining quality muscle mass and simply adding unnecessary weight.
Let’s break down the science of bodybuilding nutrition.
Factors That Determine Caloric Requirements
You’ll need to understand your specific caloric requirements before designing an effective bodybuilding nutrition plan.
Your daily calorie needs depend on several key factors, including your current body weight, training intensity, and whether you’re bulking or cutting.
Just as Arnold Schwarzenegger adjusted his intake between competition seasons, you’ll need to modify your calories based on your changing goals and activity levels.
Understanding Caloric Needs
When it comes to building an impressive physique like Arnold Schwarzenegger’s, understanding your caloric needs is the foundation of successful bodybuilding.
Your total daily energy expenditure depends on key factors like your weight, height, age, and activity level. To pack on muscle mass like the Austrian Oak, you’ll need to maintain a calorie surplus, not a calorie deficit.
Your calorie intake should prioritize nutrient-dense foods to support ideal muscle growth. Just as Arnold meticulously tracked his nutrition during his Mr. Olympia days, you’ll need to calculate your specific needs accurately.
Focus on consistent protein intake throughout the day, aiming for 1.6-2.2 grams per kilogram of body weight.
Remember, building muscle requires both strategic training and precise nutritional planning – there’s no shortcut to success.
Calculating Caloric Needs

Understanding your caloric needs forms the foundation of any successful bodybuilding journey. To calculate your requirements, you’ll need to determine three essential numbers:
- Your basal metabolic rate (BMR)
- Total daily energy expenditure (TDEE)
- Necessary caloric surplus or deficit
Start by calculating your TDEE, which combines your BMR with your activity level. For maintenance, stick to your TDEE. When bulking, add 250-500 calories above your TDEE to support muscle gain.
For cutting phases, reduce your caloric intake by 250-500 calories below TDEE to promote fat loss.
Monitor your weight regularly and adjust your maintenance calories based on results. If you’re gaining too quickly during a bulk or losing too slowly during a cut, fine-tune your caloric intake accordingly.
Timing and Distribution of Nutrients
You’ll maximize your muscle-building potential by strategically timing when you eat your calories throughout the day.
While the total amount of calories matters most, spreading your meals across 4-6 eating windows helps maintain steady nutrient availability for muscle growth.
Your body’s ability to synthesize muscle protein peaks in the hours after training, so you’ll want to make certain you’re getting adequate protein and carbohydrates during this vital window.
Nutrient Timing for Muscle Gain
Proper nutrient timing can dramatically enhance your muscle-building results, just as Arnold Schwarzenegger famously emphasized the importance of “feeding the muscle” at precise intervals.
You’ll want to fuel your muscles strategically throughout the day to maximize protein synthesis and support continuous muscle growth.
Here’s what you need to know about key nutrient timing:
- Consume protein and carbs within 60 minutes after your workout to replenish glycogen stores
- Space your meals every 3-4 hours to maintain a steady nutrient flow
- Include balanced portions of protein, carbs, and healthy fats at each meal
This structured approach to meal frequency and dietary habits guarantees your muscles receive constant nourishment.
Balanced Meal Distribution
When building muscle mass, dividing your daily calories into strategically timed meals can make the difference between mediocre and exceptional gains.
To optimize muscle protein synthesis, you’ll need to distribute your macronutrient ratio across 5-6 meals throughout the day.
Space your meals 3-4 hours apart, ensuring each contains:
- 30-40g protein sources (chicken, fish, or whey)
- 40-60g complex carbs (brown rice, sweet potatoes)
- 10-20g healthy fats (nuts, avocados)
This structured approach supports your weight training efforts by maintaining steady energy levels and promoting continuous body weight gains.
As Arnold always emphasized, dietary changes are just as vital as lifting. By following this meal timing strategy, you’re providing your muscles with the consistent nutrients they need to grow and recover effectively.
Additional Factors Affecting Caloric Needs
Your sleep quality and recovery periods directly impact how many calories you’ll need to support muscle growth and repair.
If you’re not getting adequate rest, you’ll likely need more calories to compensate for your body’s reduced efficiency in processing nutrients and building muscle.
While supplements can help fill nutritional gaps, they shouldn’t be relied upon as a substitute for proper caloric intake from whole food sources.
Sleep, Recovery, and Supplements
Achieving ideal muscle growth requires more than just counting calories and lifting weights – quality sleep and strategic recovery are essential components that directly impact your nutritional needs.
When you’re sleep-deprived, your body produces excess cortisol, which can break down muscle tissue and interfere with your caloric utilization.
To optimize your results, you’ll need 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night, combined with proper supplementation.
Consider incorporating whey protein and creatine into your routine, as these supplements support muscle protein synthesis.
You’ll also want to include recovery techniques like foam rolling and stretching to maintain muscle function and prevent soreness.
Calories for Bulking (Muscle Gain)

The path to building substantial muscle mass starts with a strategic caloric surplus that supports your body’s growth demands.
You’ll need to consume 250-500 calories above your maintenance level while maintaining proper macronutrient ratios.
Focus on high protein consumption, aiming to distribute your meals throughout the day for ideal nutrient absorption.
To maximize lean muscle gains while minimizing fat accumulation:
- Calculate your maintenance calories first
- Add your strategic surplus (start with 250 calories)
- Prioritize protein intake (1-1.5g per pound of body weight)
- Space 4-6 meals evenly throughout the day
- Monitor your progress weekly
Calories for Cutting (Fat Loss)
While building muscle requires a caloric surplus, successful fat loss demands a strategic reduction in daily calories.
You’ll need to create a caloric deficit of 250-500 calories below your maintenance level to shed fat while preserving muscle mass.
To determine how you’re cutting calories, use a macronutrient calculator and follow these dietary guidelines:
- Maintain a high protein intake (1g per pound of bodyweight)
- Keep carbs moderate for energy and workout performance
- Include healthy fats for hormone function
Remember that resistance training remains essential during weight loss phases.
Your body will tap into fat stores for energy while the protein and workouts protect your hard-earned gains.
Calories for Maintenance
Successfully maintaining your physique requires finding the sweet spot where caloric intake matches your total daily energy expenditure (TDEE).
To maintain your hard-earned muscle while staying lean, you’ll need to track both your caloric intake and lean body mass consistently.
Focus on nutrient-dense foods to support muscle preservation, and distribute your macronutrients evenly throughout the day.
You’ll want to continue your resistance training routine while monitoring your body fat levels to guarantee you’re maintaining the right balance.
Key maintenance guidelines:
- Match your daily calories to your TDEE
- Monitor lean body mass changes weekly
- Keep protein intake high
- Stay consistent with workouts
- Adjust calories if you notice unwanted changes in body composition
To Wrap It All Up
You’ll find success in bodybuilding by carefully tracking your calories and adjusting based on your goals. While some might argue that counting calories is too restrictive, think of it like Arnold’s famous “blueprint for success” – precision leads to results.
Whether you’re bulking at a surplus or cutting at a deficit, remember to fuel your body with quality nutrients and stay consistent with your intake. Monitor your progress weekly and make strategic adjustments.
FAQs
How Many Calories Should I Eat per Day for Bodybuilding?
Eat 2,500 to 3,200 calories per day for bodybuilding, depending on body weight, training intensity, and metabolism. A lean bulk may need 15–18 calories per pound of body weight, while cutting requires 12–14 calories per pound to maintain muscle while losing fat.
What Factors Determine Calorie Needs for Muscle Growth?
Calorie needs for muscle growth depend on body weight, activity level, training intensity, metabolism, and recovery rate. A larger body mass and higher training frequency increase energy requirements, while slower metabolism and lower activity reduce them. Protein intake and sleep also influence growth efficiency.
Do You Need More Calories for Bulking vs. Cutting?
The main difference between bulking and cutting is calorie intake. Bulking requires a surplus of 250–500 calories per day to build muscle, while cutting needs a deficit of 300–500 calories per day to reduce fat while preserving lean mass. Training style and body composition affect adjustments.
What Are Some High-Calorie Foods That Are Good for Building Muscle?
High-calorie foods for building muscle include oats, rice, whole eggs, peanut butter, olive oil, salmon, beef, avocados, nuts, and protein shakes with added carbs. These foods provide dense calories, quality protein, and healthy fats, supporting muscle growth without relying on processed junk calories.
How Many Calories Do Professional Bodybuilders Eat?
Professional bodybuilders eat 3,500 to 5,000 calories per day during bulking phases, depending on size and training load. Some heavyweight competitors may consume 6,000–7,000 calories daily. During cutting, intake drops to around 2,500–3,000 calories while keeping protein high to maintain muscle.
What Are the Best Supplements to Increase Calorie Intake for Muscle Growth?
The best supplements to increase calorie intake for muscle growth include mass gainer powders, whey protein blended with carbs, creatine with juice, and meal replacement shakes. These supplements deliver fast-digesting calories and nutrients, making it easier to reach a 3,000–4,000 calorie daily target for bulking.