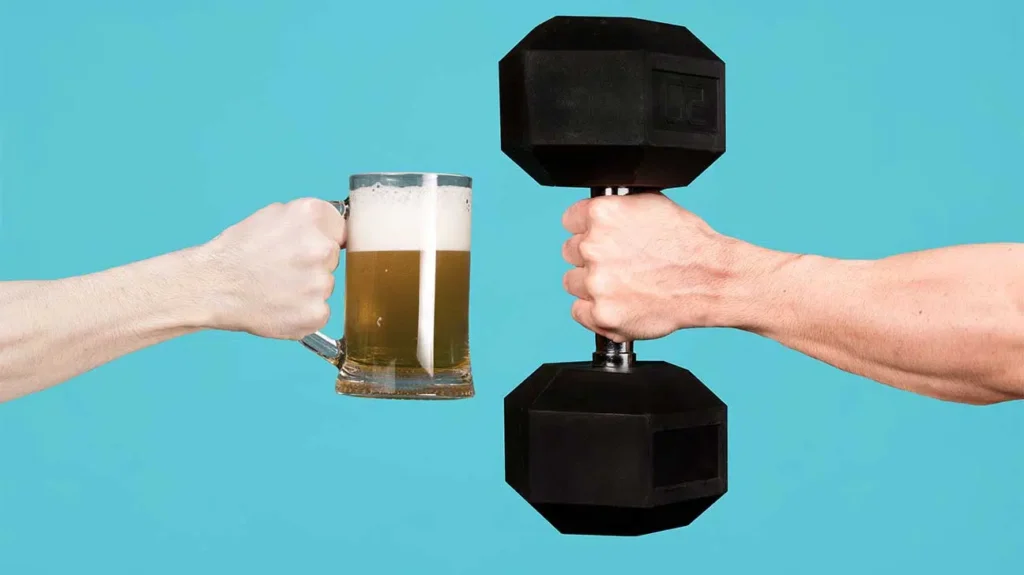
Alcohol can hinder muscle building by affecting protein synthesis and recovery. It can also dehydrate muscles, impairing performance.
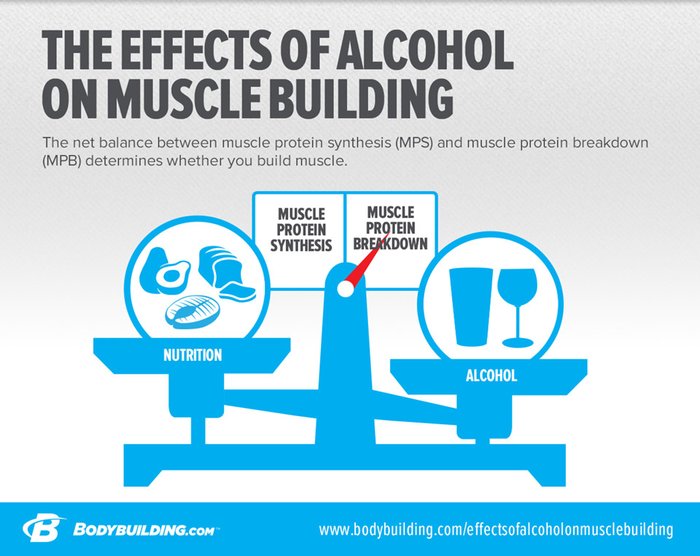
Muscle building relies on a combination of proper nutrition, regular exercise, and adequate rest. Consuming alcohol disrupts these critical factors, leading to suboptimal muscle growth. Alcohol affects protein synthesis, a key process for muscle repair and growth. It also impairs the body’s ability to recover from workouts.
Dehydration caused by alcohol can reduce muscle performance and increase the risk of injury. Limiting alcohol intake is essential for those serious about building muscle effectively. By understanding the negative impacts of alcohol on muscle development, you can make informed decisions to support your fitness goals.

Credit: alcoholcampaign.org
Alcohol’s Impact On Metabolism
Alcohol is broken down by the liver. The liver uses enzymes to process alcohol. This takes priority over other tasks. The liver stops metabolizing fats and carbs. This can lead to fat storage and weight gain.
Alcohol hinders the absorption of important nutrients. It damages the stomach lining. This makes it hard to absorb vitamins and minerals. B vitamins and zinc are especially affected. These nutrients are vital for muscle growth and repair.
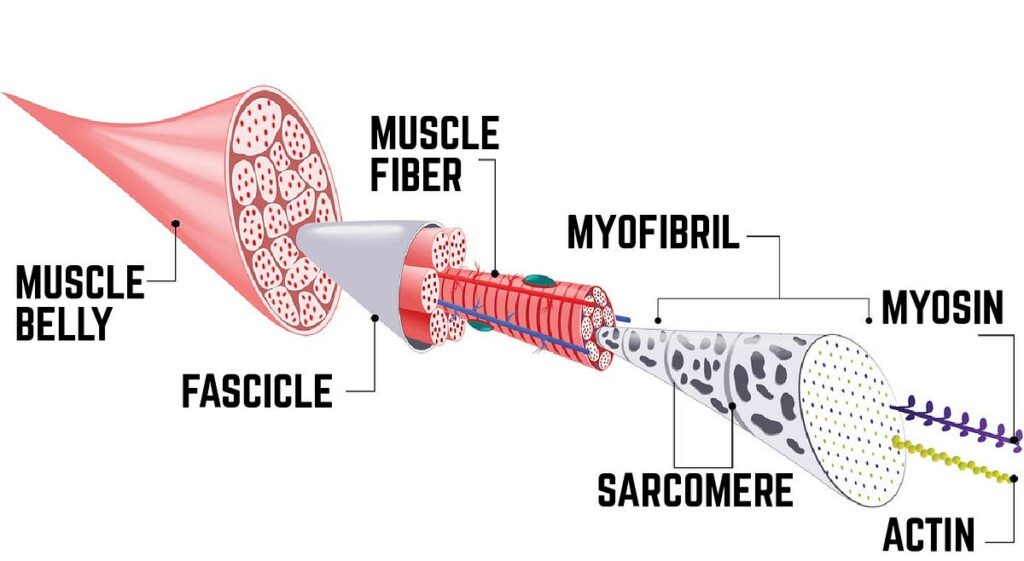
Muscle Building Basics
Muscle growth depends on several key factors. Protein intake is crucial for muscle repair. Regular exercise helps in muscle development. Rest and recovery are essential for muscle growth. Hydration plays a significant role in muscle function. Consistent strength training builds muscle mass. Balanced diet provides necessary nutrients. Adequate sleep supports muscle recovery.
Nutrition and exercise go hand in hand. Protein-rich foods like chicken and fish help build muscles. Carbohydrates provide energy for workouts. Healthy fats are important for overall health. Strength training exercises like weight lifting are essential. Cardio exercises improve heart health. Stretching helps prevent injuries. Proper hydration aids in muscle function.
Alcohol And Protein Synthesis
Alcohol can hinder muscle growth by reducing protein synthesis. Consuming alcohol disrupts the body’s ability to build and repair muscle tissue efficiently. Limiting alcohol intake may enhance muscle-building efforts.
Impact On Muscle Repair
Alcohol can slow down muscle repair. Muscles need time to heal after workouts. Alcohol can interfere with this process. It reduces the body’s ability to repair muscle damage. This can make muscles weaker over time.
Interference With Protein Absorption
Alcohol can interfere with protein absorption. Proteins are essential for muscle growth. Alcohol affects how proteins are absorbed in the body. This can lead to less muscle gain. Drinking too much alcohol can make it hard to build strong muscles.

Credit: www.muscleandstrength.com
Hormonal Changes
Alcohol can hinder muscle growth by affecting hormonal balance. It reduces testosterone levels and increases cortisol, leading to muscle loss. Drinking excessively may sabotage efforts to build muscle efficiently.
Testosterone Levels
Alcohol can lower testosterone levels in the body. This hormone is crucial for muscle growth. Lower levels can make it harder to build muscle. Drinking often can have long-term effects. It’s best to limit alcohol if you want to grow muscles.
Cortisol And Stress Hormones
Alcohol increases cortisol and other stress hormones. High cortisol levels can break down muscle tissue. This makes muscle building more difficult. Stress hormones can also affect your workout performance. Reducing alcohol can help keep cortisol levels in check.
Sleep Quality
Consuming alcohol negatively impacts sleep quality and muscle recovery. Poor sleep hinders the body’s ability to build and repair muscles effectively. Reducing alcohol intake can improve both sleep and muscle growth.
Importance Of Sleep For Muscle Growth
Sleep is crucial for muscle growth. Muscles repair and grow during sleep. Deep sleep boosts muscle recovery. Without enough sleep, muscles don’t recover well. Growth hormone releases during sleep. This hormone helps muscles grow. Lack of sleep lowers this hormone. Poor sleep can lead to weaker muscles. Strong muscles need good rest. Consistent sleep is key for muscle building.
Alcohol’s Effect On Sleep Patterns
Alcohol disrupts sleep patterns. It can make falling asleep easier. But it reduces deep sleep stages. Deep sleep is vital for muscle recovery. Alcohol can cause frequent wake-ups. This leads to poor sleep quality. Less deep sleep means less muscle repair. Drinking alcohol can delay muscle growth. For strong muscles, avoid alcohol before bed. Quality sleep is essential for muscles.
Research Findings
Some studies show that alcohol can harm muscle growth. Alcohol reduces protein synthesis, which is important for building muscles. It can also lower testosterone levels. Testosterone is a key hormone for muscle building. Drinking alcohol can lead to dehydration. Dehydration affects muscle recovery and performance. These studies suggest limiting alcohol for better muscle gains.
Not all studies agree on alcohol’s impact on muscles. Some research shows moderate drinking has little effect. These studies suggest small amounts of alcohol do not harm muscle recovery. But heavy drinking still shows negative effects. The difference in findings may depend on amount and frequency of alcohol consumption. It’s best to find a balance for overall health.
Practical Recommendations
Drink alcohol in moderation to avoid harming muscle growth. Limit to one or two drinks per day. Choose low-calorie drinks like light beer or wine. Avoid high-sugar cocktails that add extra calories. Spacing out drinks helps the body recover. Drink water between alcoholic beverages to stay hydrated.
Water is the best choice for staying hydrated. Drink at least eight glasses a day. Sports drinks are good for replacing electrolytes after workouts. Coconut water is a natural and hydrating option. Herbal teas provide hydration and have added health benefits. Fruit-infused water adds flavor without extra calories.
Credit: www.bodybuilding.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Does Alcohol Affect Muscle Growth?
Yes, alcohol can negatively impact muscle growth. It reduces protein synthesis, which is essential for muscle repair and growth.
How Does Alcohol Impact Muscle Recovery?
Alcohol impairs muscle recovery by dehydrating the body and reducing sleep quality. Both are crucial for muscle repair.
Can I Drink Alcohol And Still Build Muscle?
Moderate alcohol consumption may not completely hinder muscle growth. However, excessive drinking can significantly reduce your muscle-building potential.
What Is The Best Time To Avoid Alcohol For Muscle Gain?
Avoid alcohol around your workout times. Drinking alcohol post-workout can delay recovery and hamper muscle gains.
Conclusion
Alcohol can hinder muscle building by affecting protein synthesis and recovery. To maximize gains, limit alcohol consumption. Staying hydrated, eating well, and maintaining a balanced lifestyle are key. Prioritize your fitness goals for better results. Always consult with health professionals for personalized advice.
Your muscle-building journey deserves commitment and informed choices.