While you might think cutting all fats is the key to getting lean, you couldn’t be more wrong. Dietary fat plays a crucial role in your bodybuilding success, impacting everything from hormone production to muscle recovery.
Even Arnold Schwarzenegger, known for his strict dieting, never eliminated fats during his preparation for the Mr. Olympia competition. You’re about to discover exactly how much fat you need and which sources will fuel your gains.
Importance Of Dietary Fat
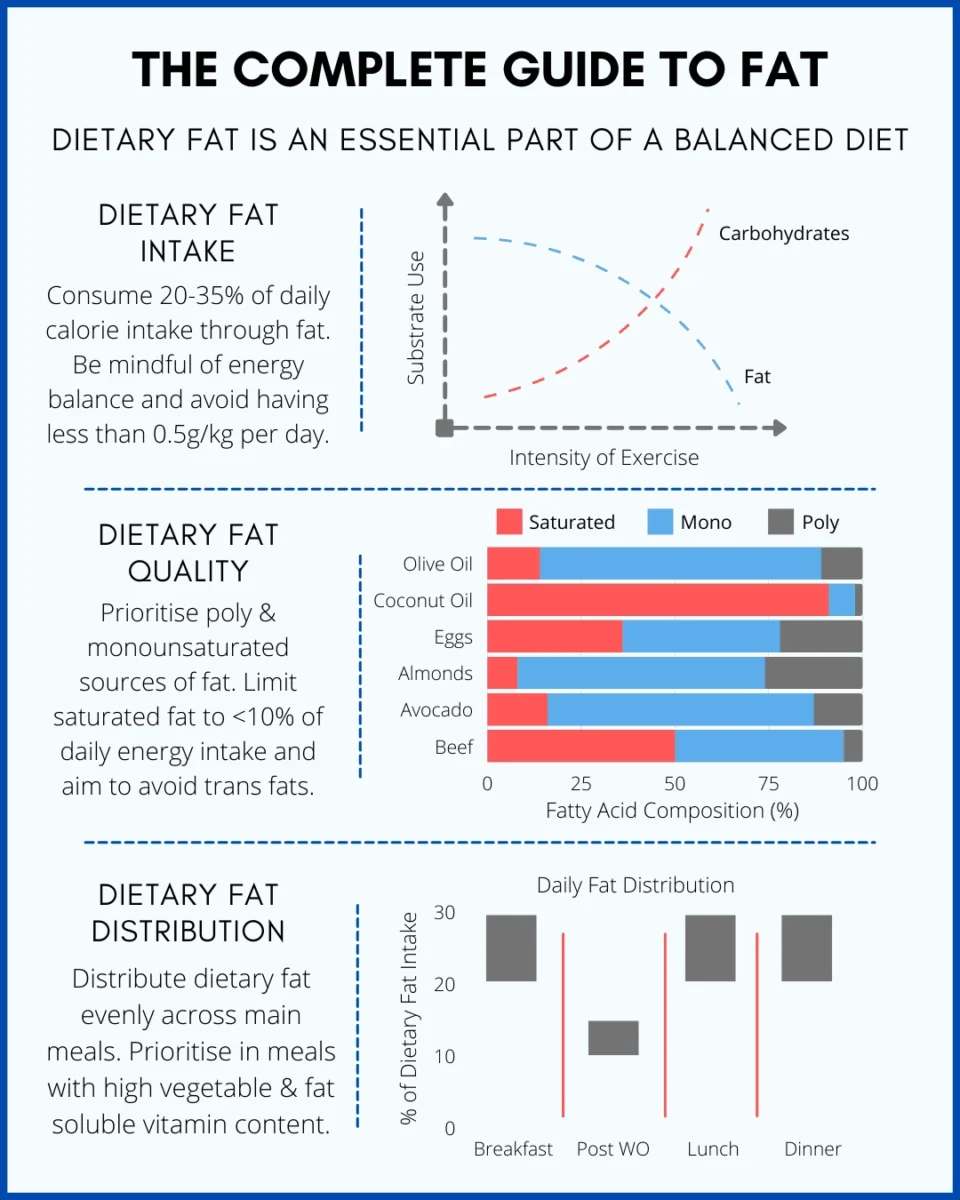
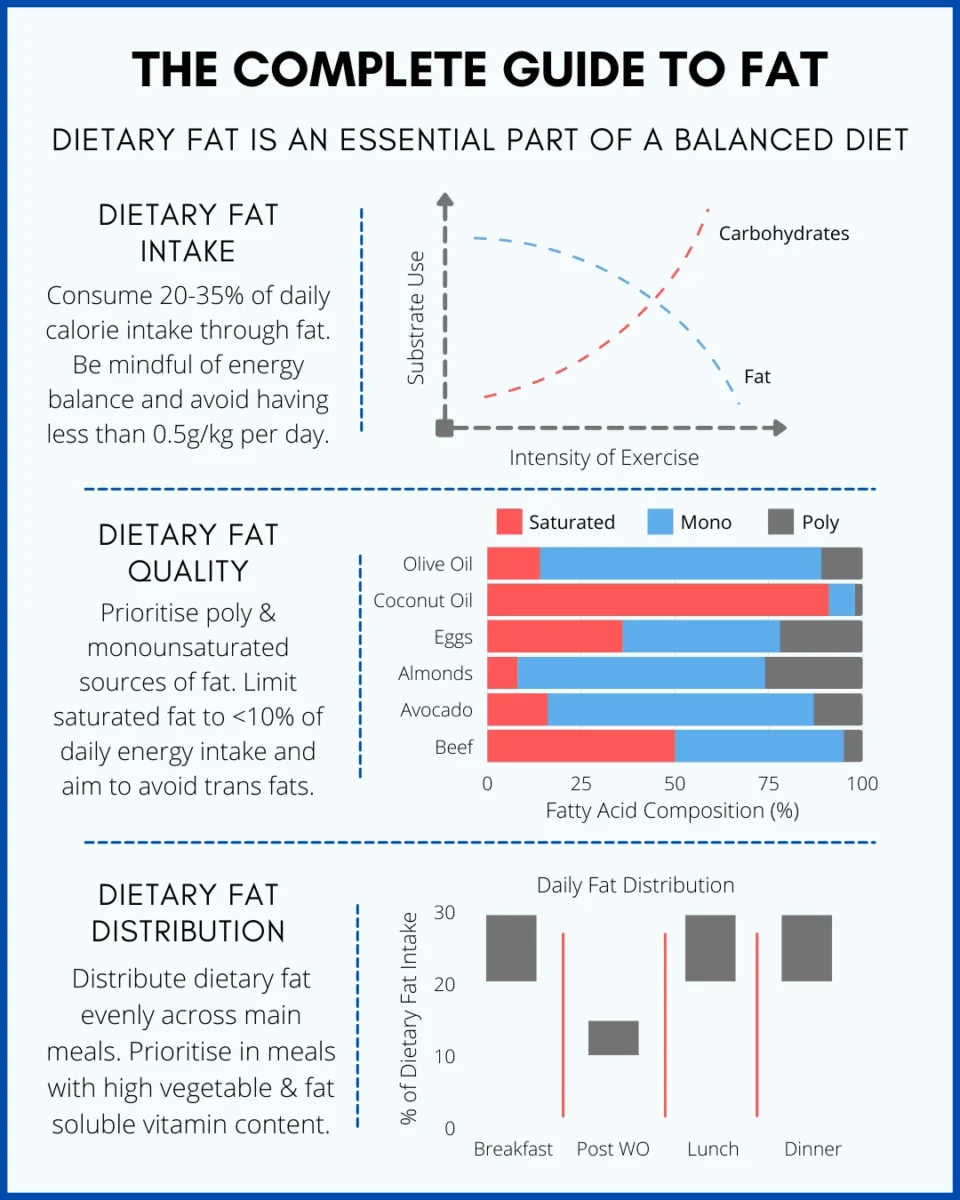
Dietary fat is crucial for making hormones. Testosterone, a key hormone for muscle building, requires fats. Low-fat intake can hurt hormone levels.
Fats give long-lasting energy. Carbs burn fast, but fats keep you going. This is vital for intense workouts. Fats help you stay strong and energized.
Daily Fat Intake Recommendations
Bodybuilders need fat in their diet. It helps with energy and hormone production. Experts suggest 20-30% of daily calories should come from fat. Eating the right types of fat is essential. Choose healthy fats, such as avocados, nuts, and fish. Avoid trans fats and excessive saturated fats.
Each body is unique. Some bodybuilders may need more or less fat. Age, weight, and activity level affect fat needs. Consulting a nutritionist can help. They can create a personalized plan. Adjusting fat intake can boost performance and recovery. Listen to your body and make changes as needed.
Fat Sources For Bodybuilders
Bodybuilders need fats for energy. Avocados are a great choice. They are rich in healthy fats. Nuts, such as almonds and walnuts, are also beneficial. They provide essential fats and proteins.
Olive oil is another excellent source. It can be used in cooking or as a salad ingredient. Fatty fish like salmon are rich in omega-3 fatty acids. These fats are good for heart health. Eggs provide a good balance of fat and protein. They are easy to prepare.
Some foods have unhealthy fats. Avoid fried foods. They contain trans fats, which are bad for health. Processed snacks like chips and cookies are high in unhealthy fats.
Fast food often has hidden fats. Margarine and shortening contain trans fats. These are bad for bodybuilding goals. Sugary foods, such as donuts, are high in unhealthy fats. They should be avoided.
Balancing Macronutrients
Bodybuilders require a balanced diet that includes a good mix of fat, protein, and carbohydrates. Each macronutrient plays a role. Protein helps to build muscles. Carbs give energy for workouts. Fat supports hormone production and overall health. Getting the right mix is key.
Many bodybuilders follow a ratio. A standard ratio is 40% carbs, 30% protein, and 30% fat. This helps maintain energy and muscle growth.
Adjust the ratio based on your goals and body type. It’s essential to track your intake. Use a food diary or a food tracking app. This will help you stay on target.
Low-Fat Diets Vs. High Fat Diets: Which Is Better?
While bodybuilding culture once promoted extremely low-fat diets, modern research indicates that maintaining an adequate intake of fat is crucial for muscle growth and overall health.
When you drastically reduce your dietary fat intake, you are likely to experience decreased testosterone levels, poor muscle recovery, and compromised body composition results.
Very low-fat diets can work against your fitness goals by elevating triglycerides and lowering good cholesterol.
Instead of fearing fat, you’ll want to adopt a balanced, healthy diet that includes a sufficient intake of dietary fat. This approach helps optimize testosterone levels, improves insulin sensitivity, and enhances muscle growth through increased mTOR pathway activation.
You’ll also experience better recovery, reduced joint pain, and improved mental well-being—all essential factors for long-term bodybuilding success.
What About Going the Opposite Route by Eating a Very High-Fat Diet?
Although eating sufficient dietary fat is essential for bodybuilding success, consuming extremely high amounts won’t provide additional benefits beyond what you’d get from moderate intake.
Once you’ve hit the necessary threshold for ideal hormone production, additional fat intake won’t boost testosterone further.
Remember that dietary fats contain 9 calories per gram, more than double that of protein and carbs.
While some bodybuilders succeed with high-fat approaches, it’s not due to any special metabolic advantages. Your body fat loss depends primarily on maintaining a caloric deficit.
If you’re considering a high-fat diet, keep in mind that it may limit your overall food choices and make it harder to meet your protein goals for muscle mass.
For most lifters, moderate-fat, sustainable diets tend to produce better long-term results.
Fat Intake For Bodybuilding: How Much Fat Should You Eat Per Day?
Finding the right amount of dietary fat can significantly impact your bodybuilding progress. For ideal results in building muscle and maintaining health, you’ll aim for about 25% of your total calorie intake to come from fat.
This balanced approach ensures you’re getting enough fat while leaving room for adequate protein and carbohydrate intake.
To calculate your daily fat intake, multiply your total daily calories by 0.25, then divide by 9. For instance, if you’re consuming 2700 calories daily, you’d need 75 grams of fat per day.
While you can go slightly higher than 25%, don’t drop below 20% of your total calories from fat, as this could hinder your progress and overall health.
What Are The Best Sources Of Fat To Eat?
When it comes to choosing the best fats for your bodybuilding diet, you’ll need to know about the four main types: Monounsaturated Fats (MUFAs), Saturated Fats (SFAs), Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids (PUFAs), and Trans Fats.
Each type of fat plays a different role in your body’s functions, from hormone production to nutrient absorption, making it essential to understand which ones to prioritize and which to limit.
Just as Arnold emphasized quality in his training, you’ll want to focus on quality fat sources while avoiding harmful trans fats that can derail your gains.
1. Monounsaturated Fat (MUFAs)
In the world of bodybuilding nutrition, monounsaturated fats (MUFAs) stand out as a powerhouse for both muscle growth and heart health.
You’ll find these beneficial monounsaturated fatty acids packed into plant oils, such as olive oil, which has been a staple of healthy Mediterranean diets for centuries.
To maximize your cardiovascular benefits while building muscle, incorporate rich sources of MUFA into your daily meal plan. Your best options include:
- Olive oil for cooking and dressings
- Avocado oil for high-heat preparation
- Natural peanut butter for pre-workout energy
- Macadamia nuts and almonds for healthy snacking
- Hazelnut oil for flavor enhancement
The health benefits of MUFAs go beyond just heart protection – they’ll help support your overall training goals while keeping your body functioning at its peak performance level.
2. Saturated Fat (SFAs)
Saturated fats have sparked fierce debate in the bodybuilding world, with opinions ranging from complete avoidance to unlimited consumption. The truth lies somewhere in between, as these fats play essential roles in your body, particularly in testosterone production.
If you’re hitting the weights regularly and following a nutrient-dense diet, you don’t need to stress about saturated fat intake. Your body will respond differently to these fats compared to sedentary individuals, especially when you’re lean and active.
You’ll find high-quality sources in animal products, such as grass-fed beef, whole eggs, and dairy.
Avoid extreme approaches when it comes to saturated fats. Instead, focus on maintaining a balanced diet with natural food sources, and you’ll get the right amount to support your muscle-building goals without compromising your health.
3. Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids (PUFAs)
Unlike other dietary fats, polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) are essential nutrients that your body can’t produce on its own.
These vital fats come in two primary forms: omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, with a preferred consumption ratio between 1:1 and 1:4.
Unfortunately, most bodybuilders consume far too many omega-6 fatty acids and not enough omega-3 fatty acids.
You’ll want to prioritize omega-3 sources for their beneficial effects on cardiovascular health, muscle recovery, and inflammation reduction.
The best sources include:
- Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines)
- Fish oil supplements (aim for 1-6g EPA/DHA daily)
- Flaxseeds and walnuts (though less efficiently converted)
While focusing on your protein consumption is important, don’t overlook these essential fats – they’re just as significant for ideal muscle growth and overall health.
4. Trans Fats
Almost everybody knows to avoid trans fats, and for good reason – they’re the worst type of dietary fat you’ll encounter in your nutrition journey.
These fats, created through the hydrogenation of vegetable oils, can wreak havoc on your physique and health.
Trans fats are associated with severe health issues, including inflammation, weight gain, heart disease, and insulin resistance.
Even consuming just 2% of your daily caloric intake as trans fats considerably increases health risks.
You’ll find them lurking in processed foods like:
- Baked goods (cakes, cookies, muffins)
- Margarine
- Fast food items
- Frozen pizzas
- Microwaved meals
Keep your trans fat intake under 2 grams daily, as recommended by the American Heart Association.
Timing Your Fat Intake
Eating fat before a workout can slow down digestion. This might make you feel sluggish. Carbs and protein are better choices. They provide quick energy and help build muscle. Small amounts of healthy fats can be acceptable. Try a little avocado or nuts. These fats won’t weigh you down.
After working out, your body needs to recover. Healthy fats can help repair muscles. They also reduce inflammation. Omega-3 fats are the best. You can find them in fish and flaxseeds. Don’t forget to add protein and carbs. They work together with fats to help you recover faster.
Common Myths
Many people think that eating fat will make them fat. This is not true. Healthy fats are essential for your body. They help build muscle and provide energy. Eating too much junk food can make you fat, not healthy fats.
Some believe that low-fat diets are the best for bodybuilding. This is a myth. Your body needs fats to work well. They help your brain and heart. Healthy fats can be found in nuts, avocados, and certain types of fish. Eating the right amount of fat enables you to stay strong and fit.
Monitoring Progress
Track your food daily. Use a journal or an app. Note down everything you eat. This helps you see your fat intake. Compare it with your goals. Ensure you get the right amount of fat.
Check your progress every week. Look at your weight and muscle growth. Adjust your fat intake if needed. Increase fats if you lack energy. Decrease if you gain too much fat. Always aim for balance.
To Wrap It All Up
You’ve now got the tools to optimize your fat intake for maximum gains, just like Arnold crushing his competition in the golden age of bodybuilding. Remember to keep your fats at 25% of total calories, choose quality sources like olive oil and salmon, and ditch those muscle-killing trans fats.
Whether you’re a weekend warrior or competitive bodybuilder, proper fat intake is your secret weapon for building a championship physique.
FAQs
How Much Fat Should a Bodybuilder Eat?
A bodybuilder should eat 15% to 25% of their daily calories from fat. This supports hormone production, joint health, and energy balance. For a 3,000-calorie diet, that equals 50 to 83 grams of fat per day. Prioritize healthy fats like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil.
Is Fat Important for Muscle Growth?
Yes, fat is important for muscle growth because it supports hormone production, including testosterone, which aids in muscle development. Dietary fat also provides energy and helps absorb fat-soluble vitamins essential for recovery and performance.
Does Fat Intake Affect Testosterone?
Yes, fat intake affects testosterone levels. Diets with moderate to high fat—especially those including monounsaturated and saturated fats—can help maintain or boost testosterone. Very low-fat diets may reduce testosterone production, impacting strength and muscle gain.
Is Saturated Fat Bad for Bodybuilders?
Saturated fat is not inherently bad for bodybuilders when consumed in moderation. It supports testosterone levels and energy production. However, excess intake may increase heart disease risk. Bodybuilders should balance saturated fats with unsaturated fats from sources like olive oil, nuts, and fish.
Are Low-Fat Diets Good for Bodybuilders?
Low-fat diets are generally not ideal for bodybuilders. Fat is essential for hormone production, recovery, and energy. Diets too low in fat can reduce testosterone, impair performance, and slow muscle growth. A balanced intake of healthy fats improves training outcomes and supports overall health.
Fat Macros for Bodybuilding – How to Calculate?
Calculate fat macros for bodybuilding by multiplying total daily calories by 0.15 to 0.25. For a 3,000-calorie diet, this equals 50 to 83 grams of fat per day. Prioritize fats from whole foods like olive oil, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish to support hormone levels and recovery.