Strength training enhances swimmers’ performance by boosting strength, endurance, and injury prevention. It complements swim workouts for optimal results.
Strength training is essential for swimmers aiming to improve their performance in the pool. It helps build muscle strength, which translates to more powerful strokes and faster swim times. Additionally, strength training can improve endurance, allowing swimmers to maintain their speed over longer distances.
Consistent strength workouts reduce the risk of injuries by balancing muscle groups and enhancing overall body stability. Swimmers should incorporate exercises targeting core, upper, and lower body muscles for a well-rounded training regimen. Examples include squats, planks, and pull-ups. By integrating strength training, swimmers can achieve peak physical condition and excel in their competitions.
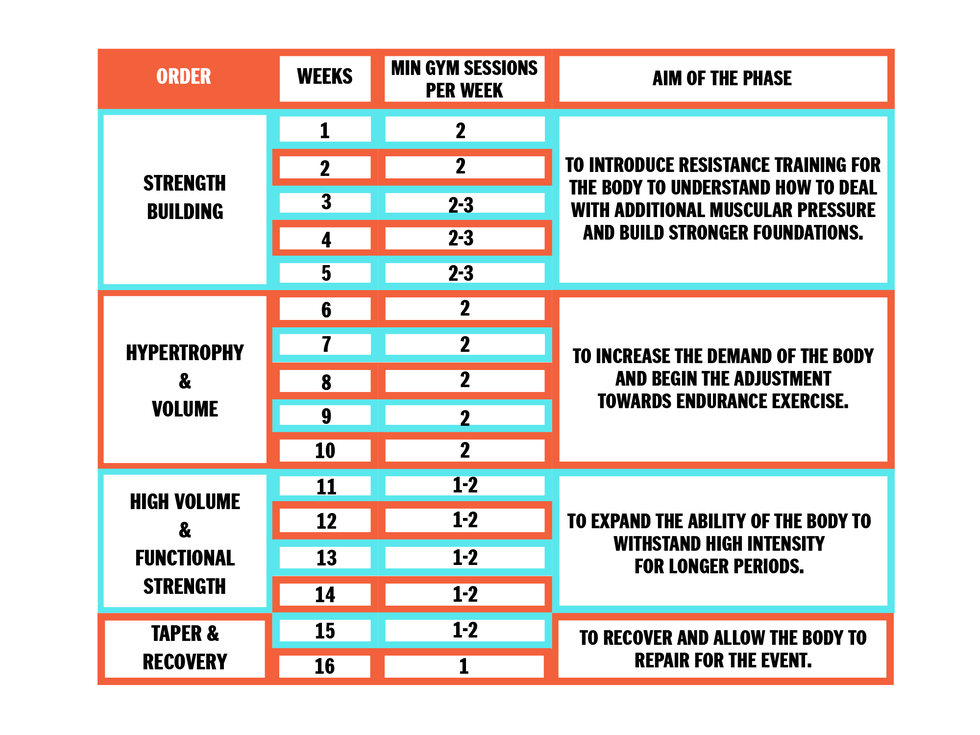
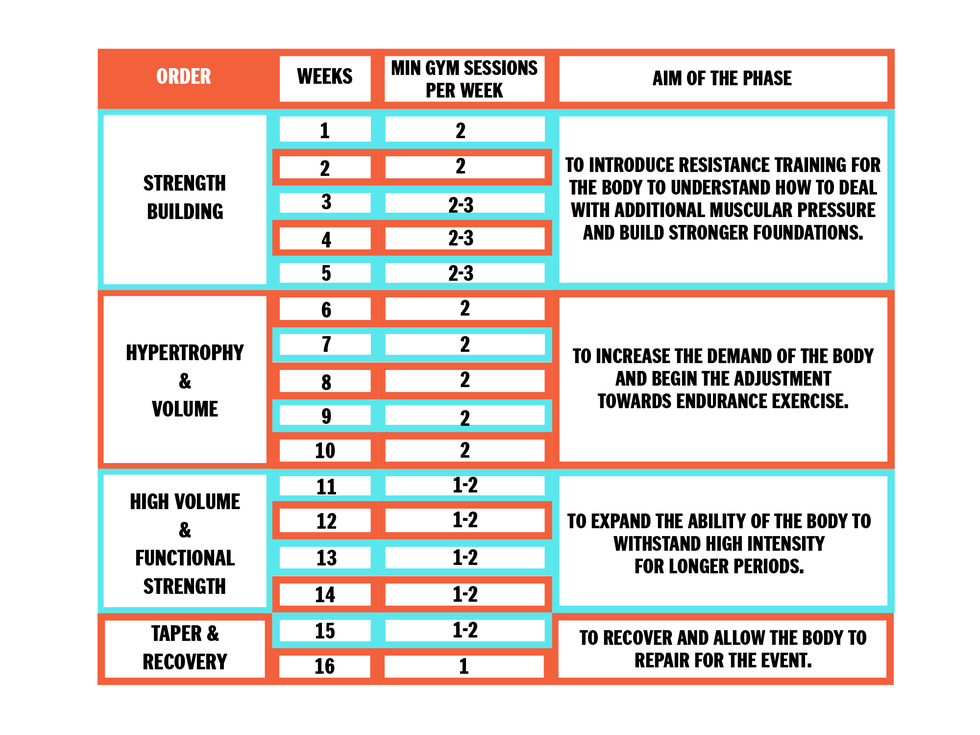
The Importance Of Strength Training For Swimmers
Strength training helps swimmers swim faster. Strong muscles improve swimming technique. Improved technique means less water resistance. Less resistance leads to better speed. Good strength also boosts endurance. Swimmers can swim longer without getting tired.
Strong muscles protect joints from injury. Swimmers with strong muscles get injured less. Less injuries mean a longer swimming career. Strength training also helps maintain bone health. Healthy bones support overall body strength.
Anatomy Of A Swimmer’s Body
Swimmers need strong shoulders and back muscles. These muscles help in powerful strokes. Core strength is also vital. It stabilizes the body in water. Strong legs enhance kicking efficiency. Focus on quadriceps, hamstrings, and calves. Do not forget arms. Biceps and triceps play a crucial role in swimming.
Swimming needs both endurance and explosive strength. Training should mimic swim actions. Short, intense workouts help with speed. Long, steady workouts build stamina. Flexibility is also key. It helps with smooth and efficient strokes. Recovery is important. Muscles need rest to grow stronger. A balanced routine avoids overtraining.
Creating The Right Strength Training Program
Knowing your current fitness level is important. It helps you plan your training. Test your strength, flexibility, and endurance. Use simple tests like push-ups and planks. Measure how long you can hold them. Write down your results. This will show your progress over time.
Swimmers need both water and land workouts. Water workouts improve stamina and technique. Land workouts build muscle strength. Plan your week to include both types. For example:
| Day | Activity |
|---|---|
| Monday | Swimming |
| Tuesday | Strength Training |
| Wednesday | Swimming |
| Thursday | Strength Training |
| Friday | Swimming |
| Saturday | Rest or Light Activity |
| Sunday | Rest or Light Activity |
Core Exercises For Swimmers
Swimmers benefit immensely from core exercises that enhance stability and power. Effective strength training boosts performance and reduces injury risk. Incorporating targeted workouts into routines leads to stronger, more efficient strokes.
Stabilization And Rotation Movements
Planks are great for core stabilization. They help swimmers maintain balance in the water. Russian Twists target the oblique muscles. This improves rotation during strokes. Bird Dogs enhance overall stability. This exercise also strengthens the lower back. Side Planks focus on the obliques. They also aid in maintaining a streamlined position.
Advanced Core Training Techniques
Medicine Ball Slams develop explosive power. They are excellent for swimmers. Hanging Leg Raises target the lower abs. This exercise improves core strength. Ab Rollouts challenge the entire core. They are effective for advanced training. Bosu Ball Balance exercises enhance stability. They also improve body control.
Upper Body Workouts To Enhance Stroke Power
Shoulder strength is key for swimmers. Push-ups are simple and effective. Shoulder presses with dumbbells can help too. Swimmers should also try lateral raises. This targets the shoulder muscles well. Resistance bands can add variety to the workouts. Consistent training will lead to stronger shoulders.
Strong back and arm muscles improve swimming power. Pull-ups work wonders for the back. Bent-over rows with weights are also effective. Bicep curls strengthen the arms. Tricep dips help build arm endurance. Mixing these exercises ensures balanced muscle growth. Swimmers should focus on proper form to avoid injury.
Credit: swimswam.com
Lower Body Drills For Explosive Kicks
Building leg strength is crucial for swimmers. Squats and lunges help in developing powerful legs. Stretching exercises improve flexibility, making kicks more effective. Hamstring stretches prevent injuries and keep muscles loose. Calf raises build strength in lower legs, aiding in swift kicks.
Plyometric exercises boost speed and power. Jump squats are excellent for building explosive strength. Box jumps enhance leg power and coordination. Lateral jumps improve agility and quickness. Short and intense workouts bring the best results.
Incorporating Resistance Training
Resistance bands are great for swimmers. These bands help improve strength and flexibility. Swimmers can use them for many different exercises. They are easy to carry and use anywhere. Bands come in different levels of resistance. This helps you to progress as you get stronger. Using bands can reduce the risk of injury. They provide a safe way to build muscle. Swimmers should include them in their workouts.
Weight training helps swimmers get stronger. It is important to train safely. Always start with light weights. This helps to avoid injuries. Focus on using the right form. Good form is more important than lifting heavy weights. Take breaks between sets. This allows muscles to recover. Drink water to stay hydrated. Swimmers should also have a coach or trainer. They can help with exercises and safety.
Periodization: Timing Your Training Peaks
Swimmers use training cycles for best performance. These cycles are called macrocycles, mesocycles, and microcycles. A macrocycle lasts about a year. Mesocycles span several weeks or months. Microcycles are shorter, often a week long. Each cycle has different goals and intensity levels. This method helps swimmers peak at the right time. Swimmers avoid overtraining and injuries.
Swimmers reduce training volume before big events. This is called tapering. Tapering helps muscles recover fully. Swimmers feel fresh and strong. The taper period can last one to three weeks. Swimmers keep intensity high but do fewer reps. Rest and nutrition are key during tapering. Swimmers should sleep well and eat healthily.
Nutrition And Recovery For Swimmers
Strength training enhances swimmers’ performance by building muscle and endurance. Proper nutrition and recovery are essential for optimal results. Consuming balanced meals and getting adequate rest boosts strength and stamina in the pool.
Diet For Muscle Growth
A balanced diet helps muscle growth. Swimmers need protein for muscle repair. Include lean meats, fish, and eggs. Carbohydrates give energy. Eat whole grains, fruits, and vegetables. Healthy fats are important too. Find them in nuts, seeds, and avocados. Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated. Vitamins and minerals support overall health. Choose varied foods for a balanced diet.
Importance Of Rest And Recovery
Rest helps muscles grow. Sleep is very important. Aim for 8 hours each night. Rest days are needed to avoid injuries. Use ice packs for sore muscles. Stretching can help too. Massage aids recovery. Hydrate after workouts. Drink water and electrolytes. Nutrition supports recovery. Eat protein and carbs post-training. Listen to your body. Rest if you feel tired.

Credit: swimswam.com
Monitoring Progress And Adjusting The Program
Use a journal to track your progress. Write down the weights you lift. Note how many reps you complete. Check your improvement every week. Record any changes in strength.
Change your routine when you stop seeing progress. Switch exercises every 6-8 weeks. Add more weight if you find it easy. Reduce weight if you struggle. Listen to your body. Adjust the program for injuries.

Credit: www.swimmingworldmagazine.com
Frequently Asked Questions
How Many Times A Week Should A Swimmers Lift Weights?
Swimmers should lift weights 2-3 times a week. This enhances strength without overtraining, complementing their swimming workouts.
What Exercises Can I Do To Improve My Swimming?
To improve swimming, do dryland exercises like planks, push-ups, and squats. Swim drills like kick sets and pull sets help too. Incorporate core workouts and flexibility training.
How To Increase Resistance In Swimming?
Increase resistance in swimming by using paddles, fins, and drag suits. Incorporate resistance bands and underwater weights.
What Was Michael Phelps’ Workout Routine?
Michael Phelps’ workout routine included swimming 80,000 meters weekly, weight training, and core exercises. He trained six hours daily, six days a week.
What Are The Benefits Of Strength Training For Swimmers?
Strength training enhances muscle power, improves endurance, and reduces injury risk, leading to better swimming performance.
How Often Should Swimmers Do Strength Training?
Swimmers should do strength training 2-3 times a week to balance muscle recovery and performance improvement.
What Exercises Are Best For Swimmers?
Exercises like pull-ups, squats, and planks are excellent for building swimming-specific strength and stability.
Can Strength Training Improve Swim Speed?
Yes, it increases muscle power and endurance, which translates to faster swim speeds and more efficient strokes.
Should Swimmers Lift Heavy Weights?
Swimmers should focus on moderate weights with higher repetitions to build endurance and functional strength without bulky muscles.
Is Bodyweight Training Effective For Swimmers?
Yes, bodyweight exercises like push-ups and planks improve core strength and overall muscle balance crucial for swimming.
Conclusion
Strength training enhances a swimmer’s performance and reduces injury risk. Incorporate these exercises into your routine for better results. Consistency is key, so stay dedicated. Strength training will improve your speed, endurance, and overall swimming efficiency. Start today and witness the positive impact on your swimming journey.
Happy training!