You’ve probably heard Arnold Schwarzenegger’s famous quote about protein being the building block of muscle, and he wasn’t just flexing his knowledge. When you’re trying to build muscle, protein isn’t optional – it’s fundamental to the process.
Your muscles undergo microscopic damage during workouts, and without adequate protein, they can’t repair and grow stronger. While you might wonder if there are alternatives, the science behind muscle growth points to some surprising truths about protein’s irreplaceable role.
Role of Protein in Muscle Building
Protein stands as the fundamental building block of muscle growth, serving as your body’s primary tool for recovery and development. When you exercise, you create microscopic tears in your muscle fibers, triggering protein synthesis to repair and strengthen them.
This process, known as muscle hypertrophy, can’t occur effectively without adequate amino acids. Your body can’t produce all the amino acids it needs for muscle building on its own.
That’s why dietary protein is essential – it provides the necessary amino acids your muscles require for repair and growth.
Just as Arnold Schwarzenegger emphasized throughout his career, you need to feed your muscles the right building materials. Think of protein as the construction crew that arrives to rebuild your muscles bigger and stronger after every workout.
Can You Build Muscle Without Enough Protein?
While you can build some muscle with minimal protein intake, you’ll need a baseline amount to support your body’s muscle repair and growth processes effectively.
Your muscles require adequate protein – typically 0.8 to 1 gram per pound of body weight daily – to maintain and build new tissue, whether you’re using supplements or getting it through whole foods.
If you’re consistently training but not meeting your protein needs, you’ll likely experience slower gains, delayed recovery, and potential muscle loss, especially during caloric deficits.
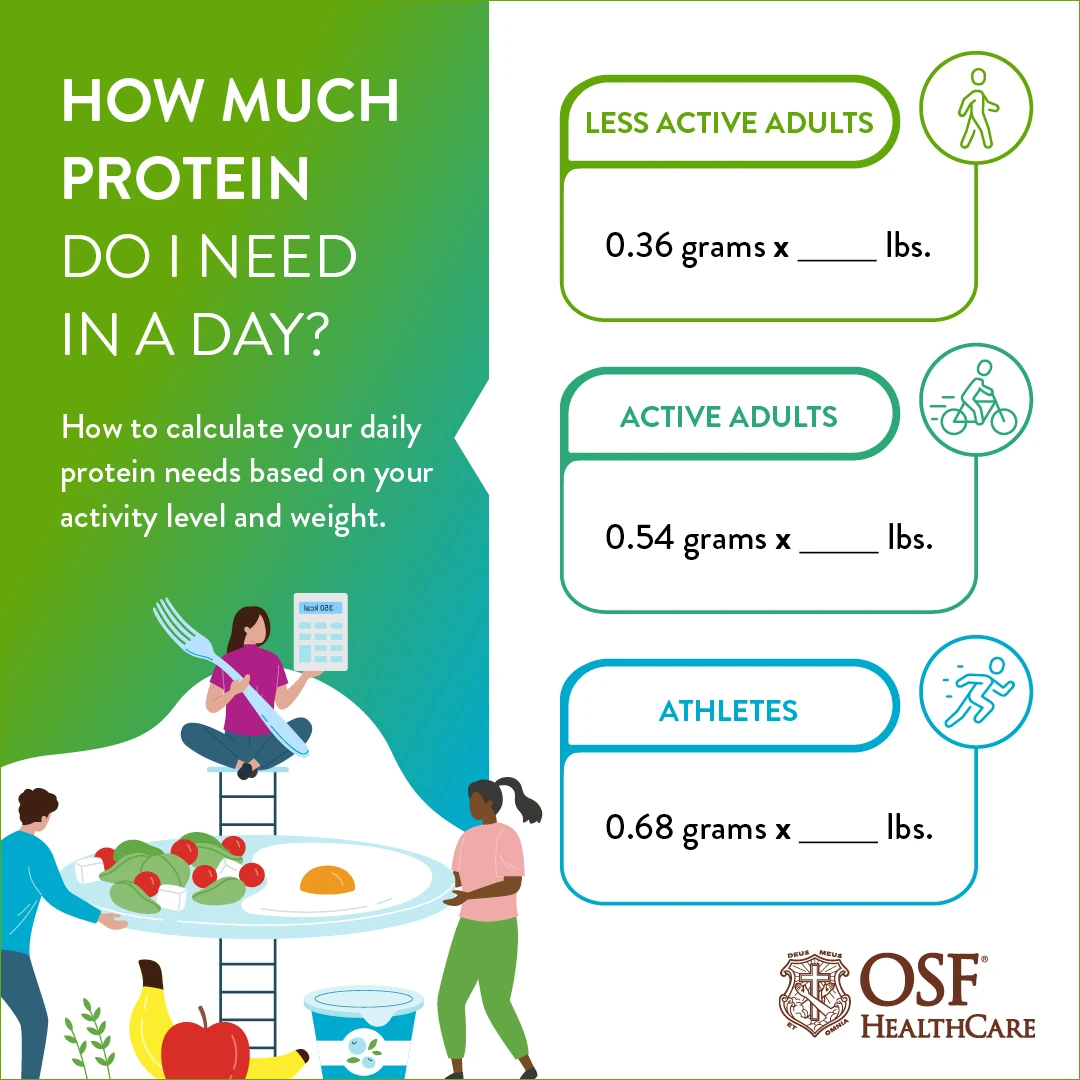
How Much Protein Does Our Body Need?
Credit: https://www.osfhealthcare.org/
You’ll need different amounts of protein based on your fitness goals and activity level, with sedentary individuals requiring less than active bodybuilders.
If you’re just starting your fitness journey or engaging in moderate workouts, you’ll want to consume more protein than someone who’s sedentary, but not as much as an advanced athlete.
For those pursuing intense bodybuilding routines like Arnold’s famous training splits, you’ll need considerably more protein to support muscle growth and recovery.
a. Sedentary lifestyle: For a sedentary lifestyle, your daily protein requirements are surprisingly modest compared to what many fitness influencers might suggest.
When you’re not actively training, your body maintains basic protein needs to preserve muscle tissue and maintain nitrogen balance.
If you weigh 70 kg (154 lbs), you’ll only need about 56 grams of protein daily – that’s less than two chicken breasts.
b. Beginner bodybuilder/moderate intensity: As your fitness journey evolves from sedentary to active training, your protein requirements naturally increase to support muscle growth and recovery.
When engaging in body weight exercises and resistance training, you’ll need 1.2 to 1.7 grams of protein per kilogram of your weight. For someone weighing 70 kg starting muscle-building activity, aim for 84-119 grams of protein daily, from both animal and plant-based proteins, to support lean tissue development.
c. Advanced Bodybuilder/Intense activity: When training reaches advanced levels of intensity, protein requirements increase substantially to support the demands of muscle hypertrophy and recovery.
As an advanced bodybuilder engaged in intense resistance exercise, you’ll need to maintain an ideal protein intake of 1.4-2.0g per kg of body weight.
Following proper dietary guidelines for Americans, focus on high-quality protein sources to maximize muscle growth potential.
What Happens If You Eat Too Much Protein?
When you consume excessive protein, you’re putting your kidneys under unnecessary strain while potentially creating dangerous nutrient imbalances in your body.
Your digestive system will struggle with the protein overload, leading to bloating, gas, and other uncomfortable symptoms that can derail your training.
The surplus protein won’t magically transform into more muscle – instead, those extra calories often end up stored as unwanted body fat, just as Arnold warned about the importance of balanced nutrition during his Mr. Olympia days.
i. Kidney problems: Understanding the relationship between protein intake and kidney health is essential for anyone pursuing muscle growth.
Your kidneys work hard to filter out nitrogen waste from protein metabolism, but excessive protein intake can overwhelm your renal functions over time.
When you consistently exceed your recommended dietary allowance, you’re putting unnecessary stress on your kidneys, potentially leading to decreased function and systemic inflammation.
ii. Nutrient imbalances: A balanced approach to muscle building requires more than just loading up on protein shakes and chicken breasts.
When you focus exclusively on protein intake, you’re likely to create nutrient imbalances by neglecting other essential food sources. Your body needs vitamins and minerals from vegetables, whole grains, and fruits to function effectively.
Without these nutrients, you’ll compromise your overall health and muscle-building potential.
iii. Weight gain: Many fitness enthusiasts mistakenly believe that eating massive amounts of protein will automatically build more muscle, but the reality works differently.
When you consume excess protein without proper strength training, those extra calories don’t magically transform into muscle fibers – they’re stored as fat.
Instead of focusing solely on optimizing protein intake, combine balanced nutrition with resistance training for effective results.
iv. Digestive discomforts: The common signs of excessive protein consumption can quickly derail your training progress.
When you consume protein-packed feasts or rely heavily on protein supplements, you’re likely to experience digestive discomfort like bloating and gas.
These uncomfortable symptoms not only make your gym sessions awkward but can also greatly impact your workout performance by causing distraction and physical discomfort.
Will I Lose Muscle if I Don’t Hit My Protein?
Maintaining adequate protein intake stands as a cornerstone of muscle preservation, making it essential to understand how protein deficiency affects your gains.
When you don’t meet your protein requirements, your body starts breaking down muscle tissue to obtain the necessary amino acids for critical functions and immune function.
While your body is remarkably resilient, consistently low protein intake can compromise tissue growth and muscle mass, especially for resistance-trained athletes.
However, don’t stress if you miss your target occasionally – a few days of suboptimal intake won’t destroy your progress. Think of protein like your muscles’ building blocks; while you need them regularly, your body can manage short-term fluctuations.
Focus on maintaining consistent protein intake through whole foods first, then supplement with protein shakes if needed to meet your daily requirements.
Is It Harder To Gain Muscle Without Protein Powder?
While protein powder offers convenience for meeting daily protein goals, you don’t need supplements to build impressive muscle mass. Your muscle gain journey can be just as successful through whole food sources that provide complete protein profiles.
Getting your protein intake from natural sources like eggs, chicken, and legumes isn’t harder – it just requires more meal planning. While protein shakes are portable and quick to prepare, you can achieve the same results by incorporating various plant proteins and animal-based options into your daily meals.
The key is consistency in meeting your protein requirements, whether through supplements or whole foods. Many successful bodybuilders built their physiques before protein powders became widely available, proving that traditional food sources can effectively support muscle growth and recovery.
9 Diet & Training Tips to Grow Muscles

If you’re struggling to build muscle, you’ll need more than just protein shakes – it’s time to overhaul your nutrition with varied protein sources, strategic meal timing, and adequate caloric intake.
Your body requires a mix of whole foods, including lean meats, eggs, fish, and plant-based proteins, combined with complex carbohydrates and healthy fats to fuel muscle growth effectively.
Just as Arnold emphasized eating like a champion to become one, you’ll need to focus on consuming nutrient-dense foods throughout the day while maintaining a slight caloric surplus to support your training goals.
1. Varied Protein Sources: A well-rounded approach to protein intake demands diverse food sources that deliver the complete amino acid profile your muscles need.
While whey protein and protein shakes are convenient, you’ll benefit more from varied protein sources like eggs, fish, and chicken.
If you follow a plant-based diet, don’t worry – lentils and nuts can provide the animal proteins your muscles require for growth.
2. Timing is Key: Timing your protein intake strategically throughout the day plays an essential role in maximizing muscle growth and recovery.
You’ll want to space your protein-rich meals evenly to maintain steady amino acids for muscle building. Consider having protein before and after workouts when your muscles need it most.
For an extra boost, try adding protein to your preworkout shakes with coffee to power through training.
3. Prioritize Calories: While protein intake remains vital, maintaining a caloric surplus serves as the foundation for building muscle mass effectively.
You’ll need to guarantee your energy balance stays positive by consuming enough calories to support muscle growth.
Even if you’re relying on plant-based protein powders and foods with a lower glycemic index, adequate caloric intake remains essential for achieving your muscle-building goals.
4. Focus on Whole Foods: Successful muscle building depends heavily on incorporating nutrient-dense whole foods into your daily diet.
While protein matters, you’ll need a balanced intake of complex carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals, and fiber to support muscle growth and maintain bone mineral density.
Focus on eating fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes to get these essential nutrients that power your workouts and recovery.
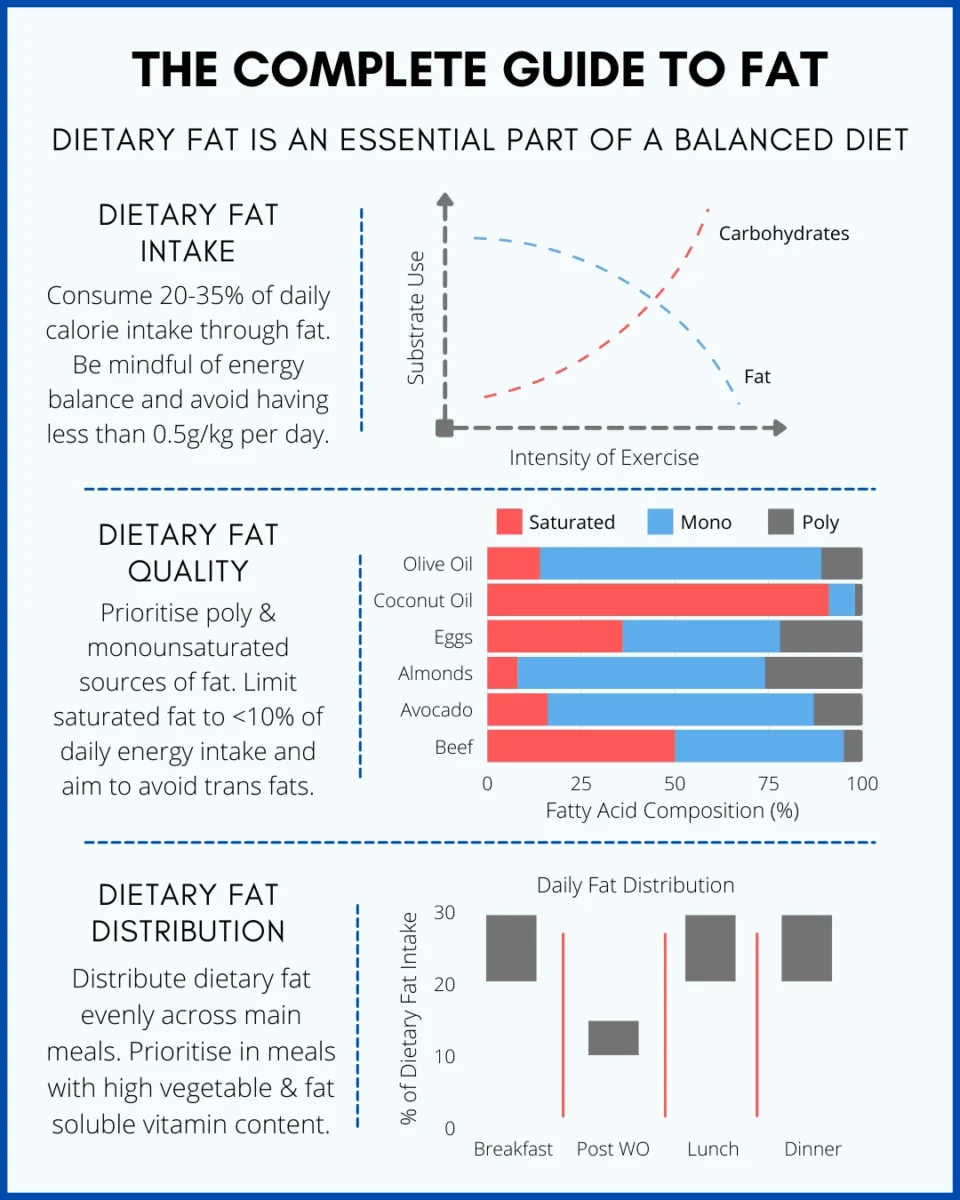
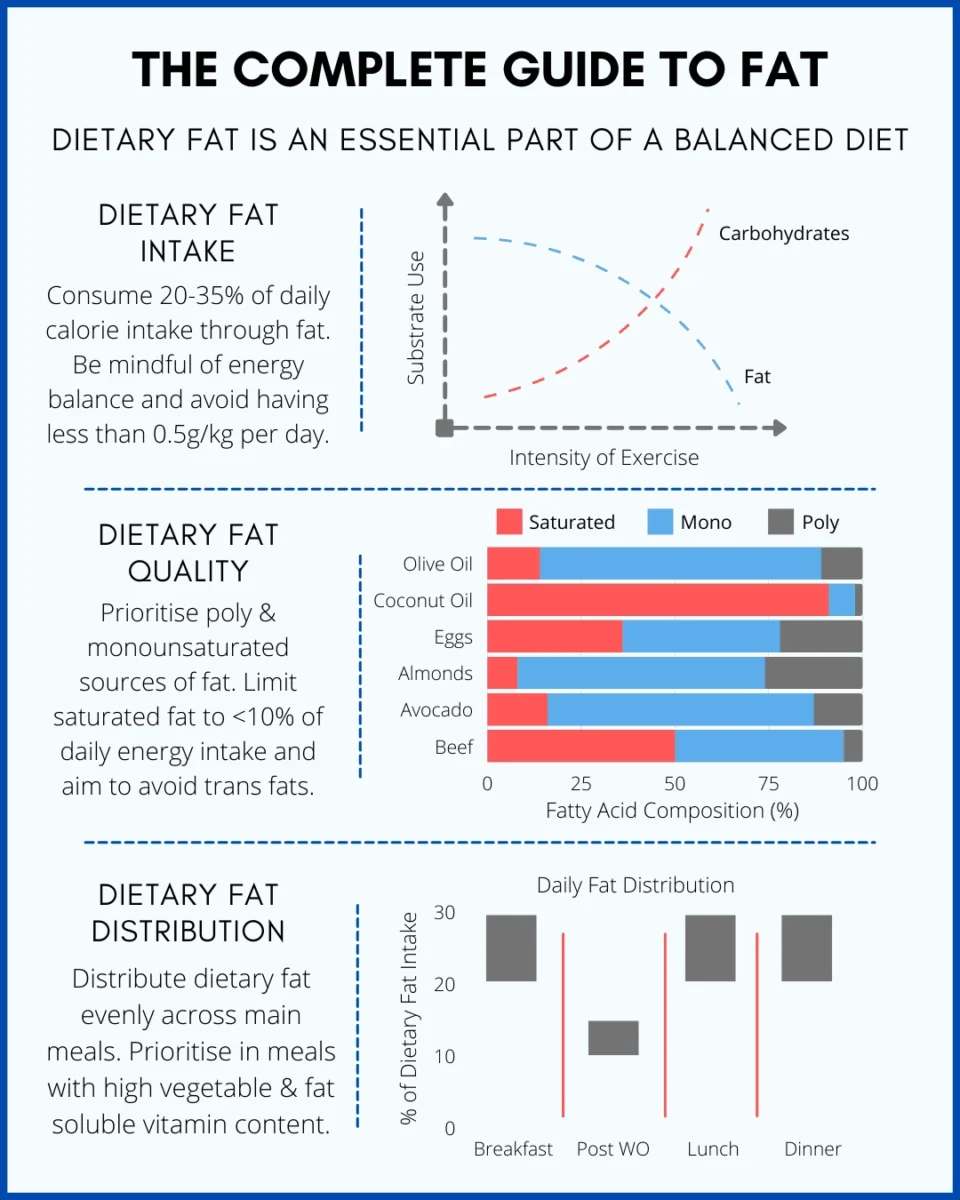
5. Carbohydrates and Fats: Although protein gets most of the attention, carbohydrates and healthy fats play vital roles in building muscle even when protein intake is lower than ideal.
Your body needs carbohydrates for energy during workouts and muscle recovery, while fats are essential for maintaining proper hormone regulation and cholesterol levels.
Without adequate amounts of both, your muscle-building progress will be limited regardless of your training intensity.
6. Hydration: Proper hydration stands as one of the three essential pillars for building muscle, alongside nutrition and training.
When you’re pushing through intense workouts in extreme heat, your skeletal muscle needs adequate water to function efficiently.
Even if you’re consuming whey concentrate and other protein sources, without proper hydration, your muscle-building efforts won’t reach their full potential.
7. Sensible Supplementation: While hydration fuels your workouts, smart supplementation can enhance your muscle-building journey.
If you’re limiting animal sources of protein, you’ll need to contemplate sensible supplementation of essential nutrients.
Key supplements to contemplate include vitamins, omega-3 fatty acids, and protein powders – these can help support muscle growth and important functions like sperm production.
8. Recovery Days: Rest days aren’t just downtime – they’re when the real muscle growth happens.
During recovery days, your body repairs and builds new muscle tissue while replenishing protein stores depleted from training.
Without proper rest between workouts, you’ll risk overtraining, which can stall your muscle-building progress.
Give your muscles time for healing by scheduling 1-2 rest days between intense training sessions.
9. Sleep: Getting adequate sleep proves vital for anyone looking to build muscle, even when following a lower-protein diet.
Your body uses sleep as its natural, hormone-free pill to repair damaged muscle tissue and optimize brain function.
When you skimp on sleep, you’re compromising muscle recovery and potentially sacrificing significant muscle gains.
That’s why quality rest is just as essential as your training.
To Wrap It All Up
You can’t build significant muscle without adequate protein – that’s the bottom line. Research shows that athletes need 1.6-2.2g of protein per kg of body weight daily for peak muscle growth.
While you don’t need expensive supplements, you must prioritize protein intake through whole foods to support your training goals. Remember Arnold’s famous quote: “Milk is for babies, when you grow up, you have to drink beer” – but we’d recommend lean protein sources instead.
FAQs
1. Can You Gain Muscle Without Protein?
You cannot gain significant muscle without protein because muscle tissue requires amino acids for repair and growth. While training may improve strength temporarily, muscle development stalls without adequate protein intake. Protein provides the essential building blocks that carbohydrates and fats cannot replace.
2. How Much Protein Do You Need To Build Muscle?
You need about 1.6 to 2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight daily to build muscle. For a 70 kg person, this equals 112–154 grams per day. Consuming protein evenly across 3–5 meals helps maximize muscle protein synthesis.
3. What Happens If You Don’t Eat Enough Protein?
If you don’t eat enough protein, your body breaks down muscle tissue for amino acids, leading to muscle loss, fatigue, and slower recovery. Low protein intake also weakens immunity and reduces hormone production, limiting strength and muscle growth potential.
4. Are Plant-Based Proteins Effective For Muscle Growth?
Plant-based proteins are effective for muscle growth when consumed in sufficient amounts and combined for complete amino acid profiles. Sources like soy, lentils, quinoa, and pea protein support hypertrophy similar to animal protein when total protein intake meets daily requirements.
5. Can Carbs or Fats Help With Muscle Growth if Protein Is Low?
Carbs and fats provide energy but cannot replace protein for muscle growth. Carbohydrates fuel training intensity, and fats regulate hormones, both supporting recovery. However, without enough protein, muscles lack the amino acids required for repair and growth, making carbs and fats insufficient alone.
6. Muscle-Building Meal Plans With Low or No Protein Shakes
A muscle-building meal plan without protein shakes can include chicken, fish, eggs, lentils, beans, quinoa, and Greek yogurt. Whole-food protein sources support hypertrophy as effectively as supplements. Distribute protein evenly across meals to meet daily needs and pair with complex carbs and healthy fats for energy.